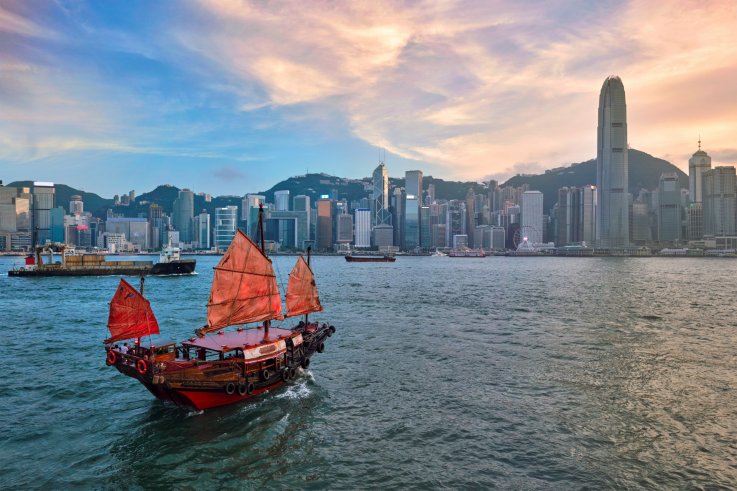
 The fate of Taiwan is not really tied up with that of Hong Kong in any direct way, although the stronger import of the one country-two systems formula, when it was first introduced, was to convince Taiwan that there would be no downside to a reunification with China proper. Hong Kong was presented with more or less the same formula, and the Taiwanese were told that all they had to do was to look to Hong Kong to see just how benign reunification would be. It is hard to see how, after the events of 2019, people on Taiwan, who, regardless of party or attitudes toward either Taiwanese or Chinese nationalism, had always been leery of pronouncements from Beijing, could ever take the blandishments of the Beijing authorities with any degree of seriousness. The behavior of the Chinese authorities toward Hong Kong may indeed insure the re-election of Taiwan president Tsai Ing-wen, whom they detest, even after all she had done to antagonize the strong support she had at the time of her election in 2016. The way the Hong Kong unrest has been handled has perhaps ended any possibility, however remote it had always been, of a peaceful reunification of Taiwan with the mainland.
The fate of Taiwan is not really tied up with that of Hong Kong in any direct way, although the stronger import of the one country-two systems formula, when it was first introduced, was to convince Taiwan that there would be no downside to a reunification with China proper. Hong Kong was presented with more or less the same formula, and the Taiwanese were told that all they had to do was to look to Hong Kong to see just how benign reunification would be. It is hard to see how, after the events of 2019, people on Taiwan, who, regardless of party or attitudes toward either Taiwanese or Chinese nationalism, had always been leery of pronouncements from Beijing, could ever take the blandishments of the Beijing authorities with any degree of seriousness. The behavior of the Chinese authorities toward Hong Kong may indeed insure the re-election of Taiwan president Tsai Ing-wen, whom they detest, even after all she had done to antagonize the strong support she had at the time of her election in 2016. The way the Hong Kong unrest has been handled has perhaps ended any possibility, however remote it had always been, of a peaceful reunification of Taiwan with the mainland.
Yet the behavior in Hong Kong is really not directly relevant to Taiwan, at least if the “formulas” presented to Taiwan are taken literally. Taiwan has been promised, like Hong Kong, full autonomy over its own political, social, and economic systems. But Taiwan, unlike Hong Kong, had a fully developed political system at the time the formula was first elaborated, one which at the time was already becoming increasingly democratic in nature and which has since grown into a fully-fledged democracy. Also, there is a promise that no civil or military officials from the mainland will be sent to Taiwan. Most importantly, Taiwan has been told that it can keep its own autonomous military. All it has to do is to accept the nominal sovereignty of Beijing.
As experience and just about anyone on the island will tell you, there is no reason to take Beijing at its word. But if Beijing tries to push its way in, as it has in Hong Kong, Taiwan, unlike Hong Kong, would have the means to push back. In effect, if the offers of Beijing to Taipei are taken literally, the power relationship between the two sides would remain just as it is now, whatever the nominal relationship. And should Taiwan defy demands from Beijing, Beijing’s only recourse would be war—just as it is now.









