Deep eutectic solvents (DESs), proven to be a unique category of material similar to but separate from ionic liquids (ILs), possess many useful properties such as high thermal stability, favorable electrochemical properties, low to no vapor pressure, strong solvation properties, and are environmentally benign. These characteristics have proven useful in a number of applications including but not limited to electrochemical storage, biomass separation and extraction, zeolite membranes, hazardous waste absorption, carbon dioxide removal, catalysis, and polymer fabrication.
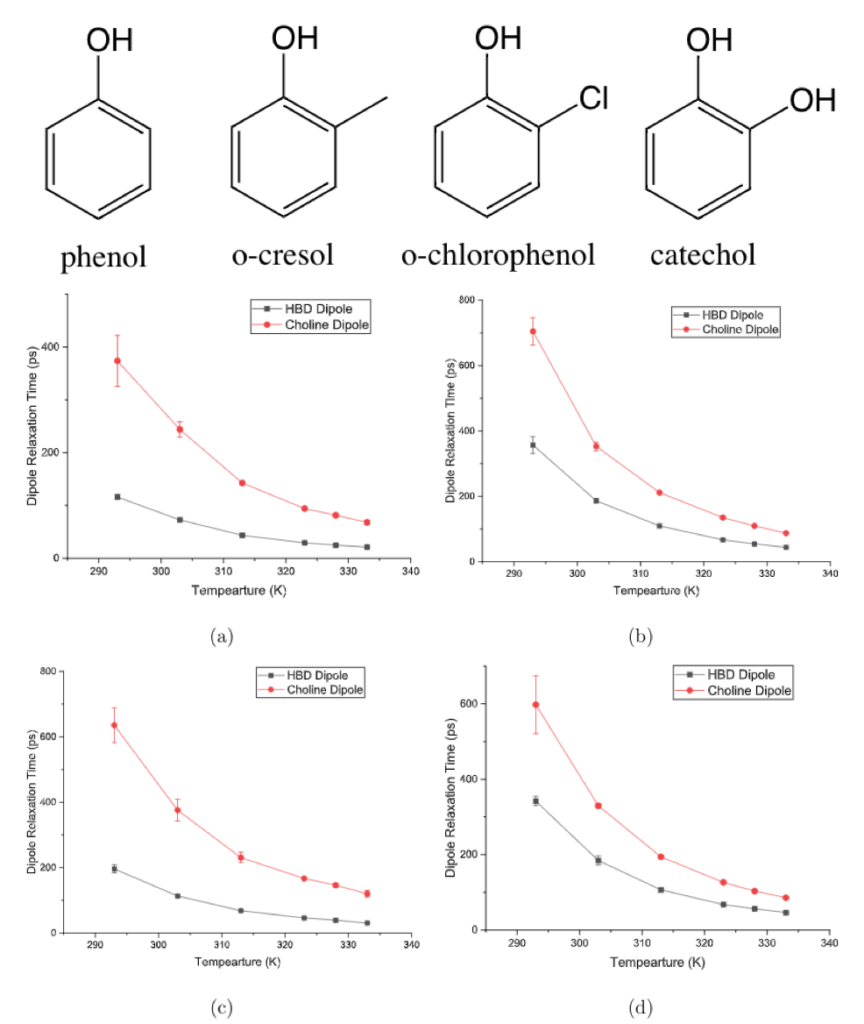
In this study, we investigated phenol-based DES systems, which provide a perfect opportunity to systematically alter hydrogen bonding donor (HBD) structure in fine changes through substitution type and positioning on the phenol ring. By comparing with experimental density and viscosity, we firstly showed that our MD model agreed well with experiments.
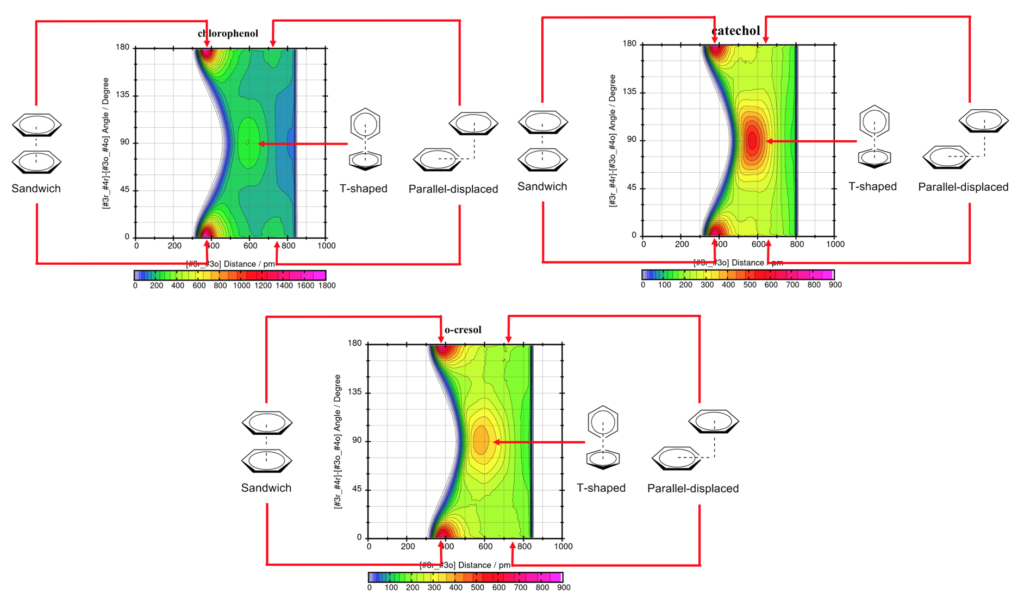
Since the phenyl group can provide ring-ring interaction, which is a main source of HBD interaction in this type of DES, we then investigated their influences on dynamic properties of fluids. We revealed that, for the phenol-based DES, its dynamic properties were highly biased by the ring-ring interaction structure.