South Bend WWTP WAS Thickening Improvements
Sponsor: Black and Veatch
Mentors: Mark Rackow, Jack and Hannah
Students: Riley Vandevelde, Joanna Nguyen-Tran, and Ashley Cernicky
Project Description:
The South Bend Wastewater Treatment Plant (WWTP) Waste Activated Sludge (WAS) Thickening Improvements Project seeks to modernize the facility’s operations by replacing outdated Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) equipment with a more efficient sludge thickening technology. This project aims to support the plant’s capacity to meet the city’s growing wastewater demands while adhering to environmental regulations. The primary goal is to create a Basis of Design Memorandum (BDM) that outlines the technical requirements and specifications for Contract Documents, which are essential for securing approval from the Department of Environmental Management (DEM).
In pursuit of a reliable replacement, the project team is evaluating several technologies, including DAF, Rotary Drum Thickening (RDT), Gravity Belt Thickener (GBT), and Centrifuge, to identify the best solution to achieve a solids concentration of 4 to 6% in sludge thickening. Key deliverables include: Project Scope, Process Flow Diagram of current situation, Technical Memorandum summarizing the analysis and recommendation, drawing production and calculations, a preliminary and final cost assessment, full table of contents with technical specifications, and a final BDM. These elements will establish a foundation for the project’s bidding documents and ensure the selected technology aligns with efficiency and sustainability goals for the WWTP’s long-term operation.

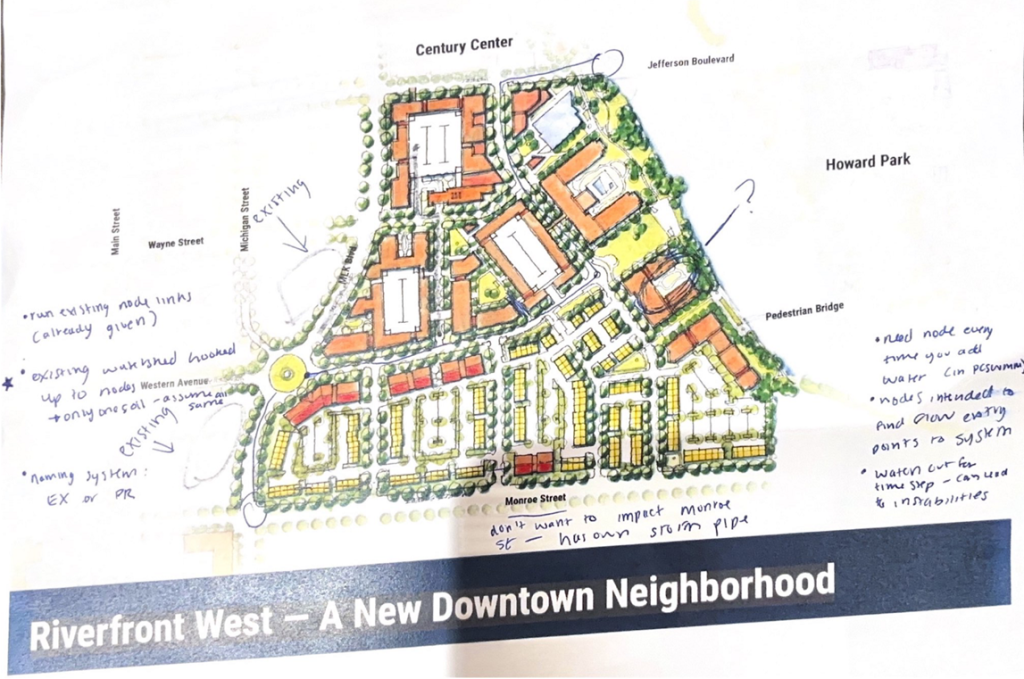
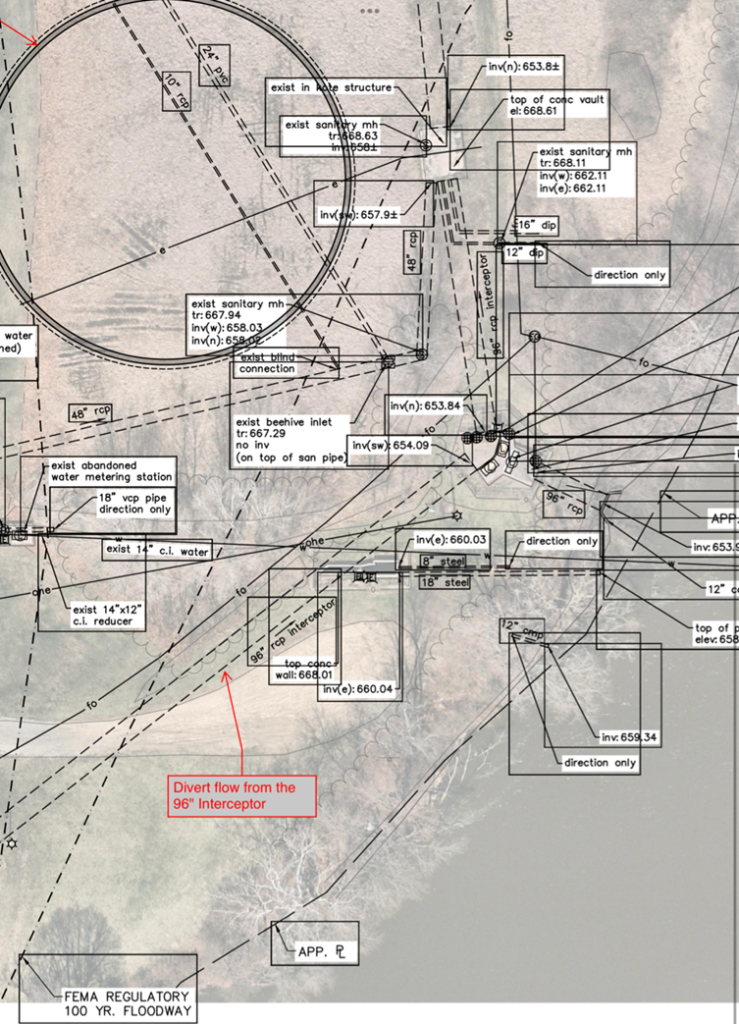
Riverfront West Stormwater System Design
Sponsor: McCormick
Mentors: Natalie Schommer-Pries and Tracy McCormick
Students: Grace Pepperman, Elena Que and Noah Salak
Project Description:
This project is focused on stormwater drainage in a small region of downtown South Bend. Currently, the area is occupied by a variety of industrial buildings and parking lots. This area drains to the St. Joseph River via a single outfall, located near Gwen Stiver Park. A new development, called Riverfront West, has been proposed in this area, featuring residential homes, amenities, and green space. The goal of this project is to develop a new stormwater drainage system for the proposed Riverfront West Development that drains to the existing single outfall on the river.
South Bend Equalization Basin
Sponsor: Structurepoint (Environment)
Mentors: Karen Saavedra
Students: Megan McGuckin, Santana Almeida, and Daniel Corcornan
Project Description:
The goal of this project is to design and construct a new equalization (EQ) basin at the South Bend Wastewater Treatment Plant in South Bend, Indiana. The design will include a pump station, diversion chamber, and new outfall structure. The EQ basin is already constructed, thus we are not responsible for the design of the EQ basin itself. The city of South Bend has a combined sewer system (CSO) that is at risk of overflowing during large rain events. In 2011, South Bend reached an agreement with the EPA to make $509.5 million worth of improvements to the combined sewer system. South Bend currently discharges over 2 billion gallons of raw sewage into the river over the course of 80 rainfall events each year. The service goal of the equalization basin will be to minimize contamination of the St. Joseph River during large storms by reducing the amount of raw sewage discharge events into the river by 95%. This project will improve the quality of the river and allow it to be a community space for the city once again. During a storm in which the flow through the sewer is >100 MGD, the diversion chamber will use weirs to divert flow from the WWTP to the EQ basin by means of the pump station. The EQ basin can hold 3 million gallons and in the event the EQ basin becomes overloaded or flow to the basin exceeds 40MGD the remaining flow will be diverted to the St. Joseph river through the new outfall structure. This project design primarily involves engineering hydraulic systems like weirs and pump systems, as well as modeling open channel, gravity driven flow in the sewer.
South Bend Edison Water Treatment Plant Renovation
Sponsor: United Consultants & City of South Bend
Mentors: Paul Glotzbach and Rebecca Plantz
Students: Julia Safford, Alex Castronovo, and Armani Carreon
Project Description:
The City of South Bend Water Works is collaborating with United Consulting to revamp several processes within the Edison Water Treatment Plant in South Bend, IN, which last underwent significant renovations in 2009. The project focuses on three primary areas: replacing the associated equipment within the gravity filters, upgrading the pumps for both the backwash and finished water systems, and improving the arsenic removal process along with associated arsenic waste disposal methods. The dysfunctional aerators will also be removed from the plant. The end goal of this project is to identify the most efficient and cost effective replacements for each of the aforementioned processes. This will be achieved through multiple iterations of comprehensive design deliverables which will include drawings done in AutoCAD and Bluebeam of the plant layout and processes, specifications on equipment needed in the plant, and cost estimates of the revamped systems. All deliverables will be aligned with the Drinking Water 10 State Standards and the IDEM Construction Permit requirements. Key technical skills required to complete these goals include water quality data analysis using Microsoft Excel, modeling the installation of the new processes and equipment in AutoCAD and Bluebeam, and performing cost estimations.
