ACS-Institutional Research Grant -Phase II Grant Funded to Mitigate Cardiotoxicity of Chemotherapeutics using our Nanocarriers

Excited that our phase-II proposal to the American Cancer Society’s Institutional Research Grant (ACS-IRG) program was funded. This was upon successful phase I completion of our proposal for a novel magnetically driven drug nanocarrier. We propose to use these drug nanocarriers to mitigate cardiotoxicity in the new study. The data generated by the study funded by this should set us up with good preliminary data for NIH and DOD grants. It is important to note that all this data was majority contributed to by undergraduate researchers.
———————————————————————————————————————————-

RIDING TO FIGHT KIDS’ CANCER
https://greatcyclechallenge.com/Riders/PrakashNallathamby
This September, I am taking part in the Great Cycle Challenge to fight kids’ cancer! Only 4% of the billions of dollars the government spends annually on cancer research is directed towards treating childhood cancer. Right now, cancer is the biggest killer of children from disease in the United States. Over 15,700 children are diagnosed every year, and sadly, 38 children die of cancer every week.
We need better treatment options for treating childhood cancer so that kids can be living life, not fighting for it. So I am raising funds through this challenge to help these kids and support Children’s Cancer Research Fund to allow them to continue their work to develop lifesaving treatments and find a cure for childhood cancer.
———————————————————————————————————————————-
Science Outlets are More Actively Promoting Novel Technologies to Address Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic-Stewardship
Excited that our novel approach to tackling antibiotic resistance is gaining well-deserved publicity! We need outside the box thinking to tackle this problem. Juliane Hopf advanceddoagnosticsandtherapeutics notredame antibioticresistance nanotechnology nanoscaleadvances pdnano biomimetics health nanoparticles nd
https://phys.org/news/2020-01-tackling-antibiotic-resistance-phage-mimicking-antibacterial.html
———————————————————————————————————————————-
Tackling antibiotic resistance: Phage-mimicking antibacterial core-shell nanoparticles could help
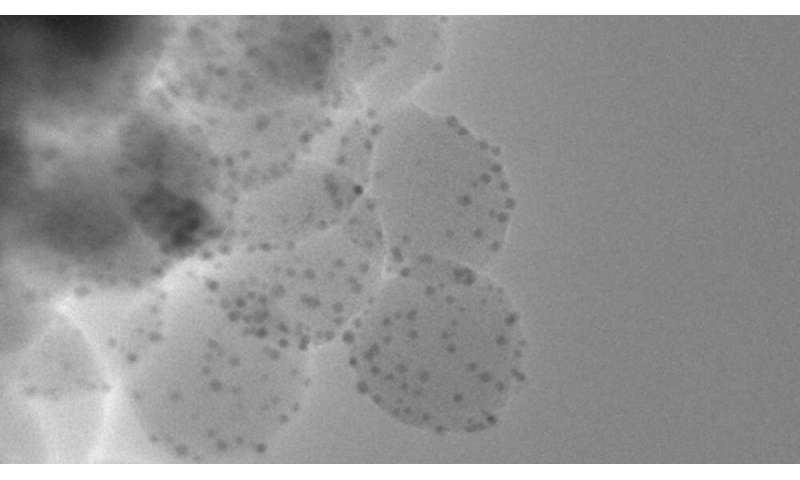
According to the World Health Organization, one of the biggest health threats around the world is antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Every day people use antibiotics to prevent or fight back against infection, but as bacteria evolve and develop resistance, diseases such as pneumonia and tuberculosis are becoming harder to treat.
“Instead of chasing the next antibiotic, we want to create a system that can treat infection and is an option that bacteria can’t develop resistance to,” said Prakash Nallathamby, research assistant professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering and directing author of the study. “In our initial attempt, our team was able to kill several different types of clinically relevant bacteria with varying degrees of success.”
The phage-mimicking nanoparticle system consists of silver-coated gold nanoparticles distributed randomly on a silica core. Once created, the system was tested for its ability to kill four bacteria types that are known to have antibiotic-resistant strains: Corynebacterium striatum, Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. These various bacteria cause a number of health issues including prosthetic device infections, sepsis, meningitis and blood infections.
Initial tests showed that the nanoparticle system was 50 percent to 90 percent effective in killing the bacteria strains for all but Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which was only 21 percent effective. However, when the researchers combined the nanoparticle system with peptides that also have antibacterial activity, the system was 100 percent effective at killing the bacteria.
“By incorporating a biological element, we were able to make the nanoparticles more effective in eliminating the bacteria in initial testing,” said Nallathamby. “Now, we are actively looking to partner with an organization that would advance this system to a clinical study.”
———————————————————————————————————————————-
Let’s Spread Awareness on Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic-Stewardship
It’s encouraging that awareness of the imminent health threat of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is rapidly increasing. We recently published our first peer-reviewed publication on phage-mimicking, broad-spectrum, antibacterial nanoparticles in RSC Nanoscale Advances (https://lnkd.in/eDGPH3s). The scientific news writeup by Brandi R. Wampler was published in ND news (https://lnkd.in/ebqPy-i). This was picked up by a New Jersey news outlet (https://lnkd.in/emUgPkR) Let’s keep spreading the awareness on the hashtagantibioticresistance problem before it gets out of hand. anitbioticsphage biomimetics nanoparticles nanotechnology ND advanceddoagnosticsandtherapeuticsnanoscaleadvances
———————————————————————————————————————————-
An Interesting Writeup on our Novel Class of Antibiotic Independent Antibacterials
According to the World Health Organization, one of the biggest health threats around the world is antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Researchers at Notre Dame are working to combat this problem by developing a nanoparticle-based system. Please check out this press release written by Brandi Wampler, our science communication specialist at Notre Dame Research.
https://news.nd.edu/news/new-technology-could-help-tackle-antibiotic-resistance/
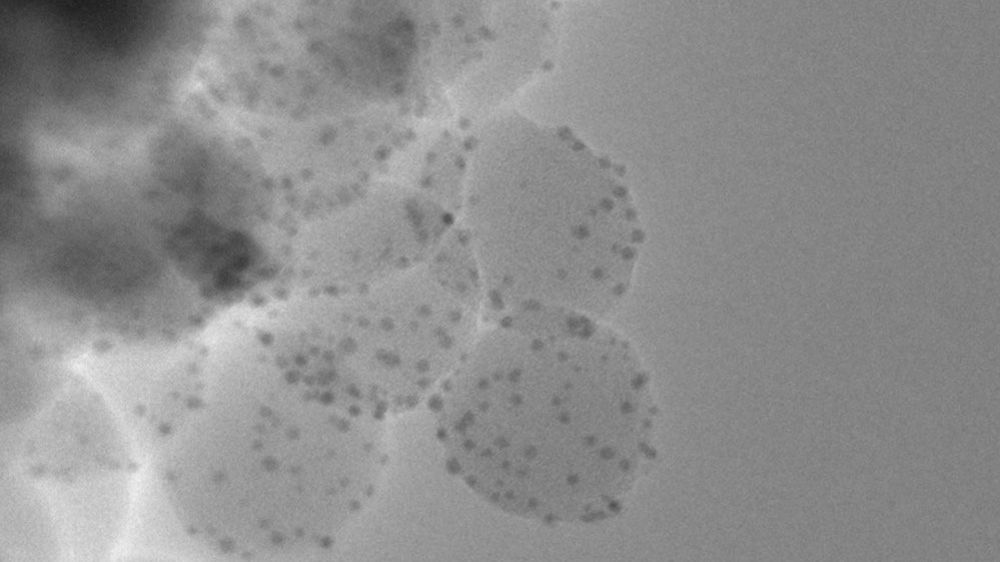
The peer-reviewed publication titled, “Phage-mimicking antibacterial core–shell nanoparticles” can be accessed at the following open-source link below.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2019/na/c9na00461k

———————————————————————————————————————————-
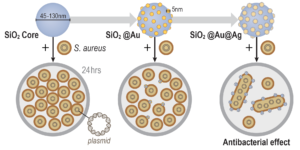
Phage-mimicking antibacterial core–shell nanoparticles
Juliane Hopf, Margo Waters, Veronica Kalwajtys, Katelyn E. Carothers, Ryan K. Roeder, Joshua D. Shrout, Shaun W. Lee and Prakash D. Nallathamby
Excited to have started publishing and filing for a patent on our antibiotic-free antimicrobial nanoparticles research. More to come in the following months! Thankful for the support from notredame ideacenter antibioticresistance ndnano Advanceddiagnosticsandtherapeutics ADandT openaccess
———————————————————————————————————————————-
Label-Free, Magnetic Nanocarrier based, Precision Combinatorial Chemotherapeutics Treatment Against Metastatic Cancer for Recurrence-Free Survival
The leading cause of fatalities in breast cancer is metastasis. To increase the success rate of metastasis-free survival, there is a need to tackle therapy-resistant metastatic forms of the disease with novel, patient-friendly, combinatorial treatment regimens. At present, doxorubicin (Dox) regimens are standard of care for tumor debulking but do not stop metastatic recurrence and present cardiotoxicity. Vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase) H+ pump inhibitors (e.g., diphyllins) prevent metastasis, but the ubiquitous occurrence of this target raises concerns of off-target toxicity. A solution is targeted delivery to reduce off-target effects while also minimizing drug dose side-effects. So, here we present the successful demonstration of targeted combinatorial-delivery of V-ATPase inhibitors (Diph) and standard chemotherapeutics (Dox) to the MDAMB231 triple negative breast cancer metastatic cell model (2D and 3D) with positive cell clearance and affirmative inhibition of cancer cell invasion. Our drug delivery system used a label-free magnetoelectric system.
Congratulations to Dr.Hopf and undergraduate researcher Margo Waters for their contributions to these excellent results.

———————————————————————————————————————————-
Society for Biomaterials 2019 in Seattle was a Success
I was in Seattle for the week at the Society for Biomaterials 2019 conference. Excited to have data from three projects in four sessions at SFB 2019. Thanks to CTSI-PDT (#CTSI), ACS-IRG(#americancersociety), NDnano, AD&T and HCRI for their crucial support for these projects.
1. Rapid-Fire oral Presentation on Wednesday on April 3, 2019, from 4:05 to 4:10 p.m. on Label-Free, Magnetic Nanocarrier based, Precision Combinatorial Chemotherapeutics Treatment Against Metastatic Cancer for Recurrence-Free Survival, during the session titled: Nanomaterials / Drug Delivery RAPID FIRE
2. An oral presentation titled: “Biomimetic Phage Mimicking Antimicrobial Nanoparticles for Antibiotic Free, Bactericidal Action Against the ESKAPE Class of Pathogens” in the session titled Recent Advances in Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Materials1 on Thursday, April 4, 2019, from 3:30 PM to 3:45 PM.
3. Poster I: (#988) Biodistribution of Cancer Stem Cells Targeting Nanoparticle Image Contrast Agents and it’s Implications in Early Diagnosis
4. Poster II: Label-Free, Magnetic Nanocarrier based, Precision Combinatorial Chemotherapeutics Treatment Against Metastatic Cancer for Recurrence-Free Survival.
The data was received very well. Onwards to publishing these interesting results this summer.


———————————————————————————————————————————-
Read our recap of a few novel ‘Blue-sky’ future applications of nanoparticles in the Biomedical Field
Over the last two decades, nanotechnology has become one of the most dynamically evolving fields of research. Various types of nanoparticles are widely exploited to extend our understanding of biological interactions at the molecular level. They are actively engaged in the biomedical research for imaging, biosensing, drug delivery and/or concurrent therapy. Recent progress on this field is briefly reviewed here with an emphasis placed on the wide imaging applications of nanoparticles. Collectively, this field will no doubt make a greater impact after we gradually address any potential risks of nanoparticles.
———————————————————————————————————————————-

RIDING TO FIGHT KIDS’ CANCER
https://greatcyclechallenge.com/Riders/PrakashNallathamby
This September, I am taking part in the Great Cycle Challenge to fight kids’ cancer! Only 4% of the billions of dollars the government spends annually on cancer research is directed towards treating childhood cancer. Right now, cancer is the biggest killer of children from disease in the United States. Over 15,700 children are diagnosed every year, and sadly, 38 children die of cancer every week.
We need better treatment options for treating childhood cancer so that kids can be living life, not fighting for it. So I am raising funds through this challenge to help these kids and support Children’s Cancer Research Fund to allow them to continue their work to develop lifesaving treatments and find a cure for childhood cancer.
———————————————————————————————————————————-
Science Outlets are More Actively Promoting Novel Technologies to Address Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic-Stewardship
Excited that our novel approach to tackling antibiotic resistance is gaining well-deserved publicity! We need outside the box thinking to tackle this problem. Juliane Hopf advanceddoagnosticsandtherapeutics notredame antibioticresistance nanotechnology nanoscaleadvances pdnano biomimetics health nanoparticles nd
https://phys.org/news/2020-01-tackling-antibiotic-resistance-phage-mimicking-antibacterial.html
———————————————————————————————————————————-
Tackling antibiotic resistance: Phage-mimicking antibacterial core-shell nanoparticles could help

According to the World Health Organization, one of the biggest health threats around the world is antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Every day people use antibiotics to prevent or fight back against infection, but as bacteria evolve and develop resistance, diseases such as pneumonia and tuberculosis are becoming harder to treat.
“Instead of chasing the next antibiotic, we want to create a system that can treat infection and is an option that bacteria can’t develop resistance to,” said Prakash Nallathamby, research assistant professor of aerospace and mechanical engineering and directing author of the study. “In our initial attempt, our team was able to kill several different types of clinically relevant bacteria with varying degrees of success.”
The phage-mimicking nanoparticle system consists of silver-coated gold nanoparticles distributed randomly on a silica core. Once created, the system was tested for its ability to kill four bacteria types that are known to have antibiotic-resistant strains: Corynebacterium striatum, Enterococcus faecalis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. These various bacteria cause a number of health issues including prosthetic device infections, sepsis, meningitis and blood infections.
Initial tests showed that the nanoparticle system was 50 percent to 90 percent effective in killing the bacteria strains for all but Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which was only 21 percent effective. However, when the researchers combined the nanoparticle system with peptides that also have antibacterial activity, the system was 100 percent effective at killing the bacteria.
“By incorporating a biological element, we were able to make the nanoparticles more effective in eliminating the bacteria in initial testing,” said Nallathamby. “Now, we are actively looking to partner with an organization that would advance this system to a clinical study.”
———————————————————————————————————————————-
Let’s Spread Awareness on Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Antibiotic-Stewardship
It’s encouraging that awareness of the imminent health threat of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is rapidly increasing. We recently published our first peer-reviewed publication on phage-mimicking, broad-spectrum, antibacterial nanoparticles in RSC Nanoscale Advances (https://lnkd.in/eDGPH3s). The scientific news writeup by Brandi R. Wampler was published in ND news (https://lnkd.in/ebqPy-i). This was picked up by a New Jersey news outlet (https://lnkd.in/emUgPkR) Let’s keep spreading the awareness on the hashtagantibioticresistance problem before it gets out of hand. anitbioticsphage biomimetics nanoparticles nanotechnology ND advanceddoagnosticsandtherapeuticsnanoscaleadvances
———————————————————————————————————————————-
An Interesting Writeup on our Novel Class of Antibiotic Independent Antibacterials
According to the World Health Organization, one of the biggest health threats around the world is antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Researchers at Notre Dame are working to combat this problem by developing a nanoparticle-based system. Please check out this press release written by Brandi Wampler, our science communication specialist at Notre Dame Research.
https://news.nd.edu/news/new-technology-could-help-tackle-antibiotic-resistance/
The peer-reviewed publication titled, “Phage-mimicking antibacterial core–shell nanoparticles” can be accessed at the following open-source link below.
https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2019/na/c9na00461k

———————————————————————————————————————————-
Phage-mimicking antibacterial core–shell nanoparticles
Juliane Hopf, Margo Waters, Veronica Kalwajtys, Katelyn E. Carothers, Ryan K. Roeder, Joshua D. Shrout, Shaun W. Lee and Prakash D. Nallathamby
Excited to have started publishing and filing for a patent on our antibiotic-free antimicrobial nanoparticles research. More to come in the following months! Thankful for the support from notredame ideacenter antibioticresistance ndnano Advanceddiagnosticsandtherapeutics ADandT openaccess

———————————————————————————————————————————-
Label-Free, Magnetic Nanocarrier based, Precision Combinatorial Chemotherapeutics Treatment Against Metastatic Cancer for Recurrence-Free Survival
The leading cause of fatalities in breast cancer is metastasis. To increase the success rate of metastasis-free survival, there is a need to tackle therapy-resistant metastatic forms of the disease with novel, patient-friendly, combinatorial treatment regimens. At present, doxorubicin (Dox) regimens are standard of care for tumor debulking but do not stop metastatic recurrence and present cardiotoxicity. Vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase) H+ pump inhibitors (e.g., diphyllins) prevent metastasis, but the ubiquitous occurrence of this target raises concerns of off-target toxicity. A solution is targeted delivery to reduce off-target effects while also minimizing drug dose side-effects. So, here we present the successful demonstration of targeted combinatorial-delivery of V-ATPase inhibitors (Diph) and standard chemotherapeutics (Dox) to the MDAMB231 triple negative breast cancer metastatic cell model (2D and 3D) with positive cell clearance and affirmative inhibition of cancer cell invasion. Our drug delivery system used a label-free magnetoelectric system.
Congratulations to Dr.Hopf and undergraduate researcher Margo Waters for their contributions to these excellent results.

———————————————————————————————————————————-
Society for Biomaterials 2019 in Seattle was a Success
I was in Seattle for the week at the Society for Biomaterials 2019 conference. Excited to have data from three projects in four sessions at SFB 2019. Thanks to CTSI-PDT (#CTSI), ACS-IRG(#americancersociety), NDnano, AD&T and HCRI for their crucial support for these projects.
1. Rapid-Fire oral Presentation on Wednesday on April 3, 2019, from 4:05 to 4:10 p.m. on Label-Free, Magnetic Nanocarrier based, Precision Combinatorial Chemotherapeutics Treatment Against Metastatic Cancer for Recurrence-Free Survival, during the session titled: Nanomaterials / Drug Delivery RAPID FIRE
2. An oral presentation titled: “Biomimetic Phage Mimicking Antimicrobial Nanoparticles for Antibiotic Free, Bactericidal Action Against the ESKAPE Class of Pathogens” in the session titled Recent Advances in Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Materials1 on Thursday, April 4, 2019, from 3:30 PM to 3:45 PM.
3. Poster I: (#988) Biodistribution of Cancer Stem Cells Targeting Nanoparticle Image Contrast Agents and it’s Implications in Early Diagnosis
4. Poster II: Label-Free, Magnetic Nanocarrier based, Precision Combinatorial Chemotherapeutics Treatment Against Metastatic Cancer for Recurrence-Free Survival.
The data was received very well. Onwards to publishing these interesting results this summer.


———————————————————————————————————————————-
Read our recap of a few novel ‘Blue-sky’ future applications of nanoparticles in the Biomedical Field
Over the last two decades, nanotechnology has become one of the most dynamically evolving fields of research. Various types of nanoparticles are widely exploited to extend our understanding of biological interactions at the molecular level. They are actively engaged in the biomedical research for imaging, biosensing, drug delivery and/or concurrent therapy. Recent progress on this field is briefly reviewed here with an emphasis placed on the wide imaging applications of nanoparticles. Collectively, this field will no doubt make a greater impact after we gradually address any potential risks of nanoparticles.
———————————————————————————————————————————-










 The poster presented by the undergraduate researchers (Margo Waters and Veronica Kalwatjys), explaining their work on a rationally designed, modular antimicrobial nanoparticle system was well received at COS-JAM 2018. Margo worked on the synthesis of the antimicrobial nanoparticles. Veronica has started testing the antimicrobial properties of these nanoparticles under the direction of Dr. Juliane Hopf. The antimicrobial peptides were sourced from Francisco Fields of Prof. Shaun Lee’s lab.
The poster presented by the undergraduate researchers (Margo Waters and Veronica Kalwatjys), explaining their work on a rationally designed, modular antimicrobial nanoparticle system was well received at COS-JAM 2018. Margo worked on the synthesis of the antimicrobial nanoparticles. Veronica has started testing the antimicrobial properties of these nanoparticles under the direction of Dr. Juliane Hopf. The antimicrobial peptides were sourced from Francisco Fields of Prof. Shaun Lee’s lab.


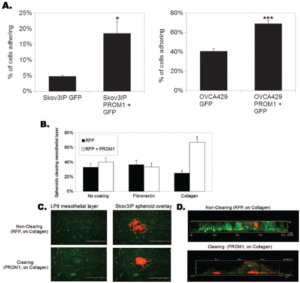




 Undergraduate Research Assistant Margo Waters (Sophomore), at her first poster presentation. Margo synthesizes the anisotropic nanoparticles being used in the ongoing study looking into the applications of antimicrobial peptides@nanoparticles as surfactants on implant materials and medical devices. The project lead is Dr. Juliane Hopf and her undergraduate mentee is Veronica Kalwatjys. The work is in collaboration with Prof. Shrout’s lab and Francisco Fields of Prof. Lee’s lab.
Undergraduate Research Assistant Margo Waters (Sophomore), at her first poster presentation. Margo synthesizes the anisotropic nanoparticles being used in the ongoing study looking into the applications of antimicrobial peptides@nanoparticles as surfactants on implant materials and medical devices. The project lead is Dr. Juliane Hopf and her undergraduate mentee is Veronica Kalwatjys. The work is in collaboration with Prof. Shrout’s lab and Francisco Fields of Prof. Lee’s lab. “Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy by stepwise optical saturation” by Yide Zhang et al.
“Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy by stepwise optical saturation” by Yide Zhang et al. 
Nallathamby Laboratory in the ‘NEWS’ for Novel Approach to CAR-T Therapy
Glad to see that our work on using nanoparticle-based ON-OFF switches for CAR-T cells therapy against solid tumors is getting positive traction in the local media. Here is my interview with Kylie Veleta of Inside Indiana business on what motivates us to keep pushing forward. The website is Indiana business focused. The interview was part of the breast cancer awareness month. The full interview can be read at http://www.insideindianabusiness.com/story/39391168/researcher-tweaks-t-cells-for-tumors
Janus nanoparticles that are being developed as ON-OFF switches for CAR-T cells in anti-caner therapy
———————————————————————————————————————————-
Nanoparticles that act as an “on and off” switch to improve the safety and effectiveness of CAR-T cancer therapy