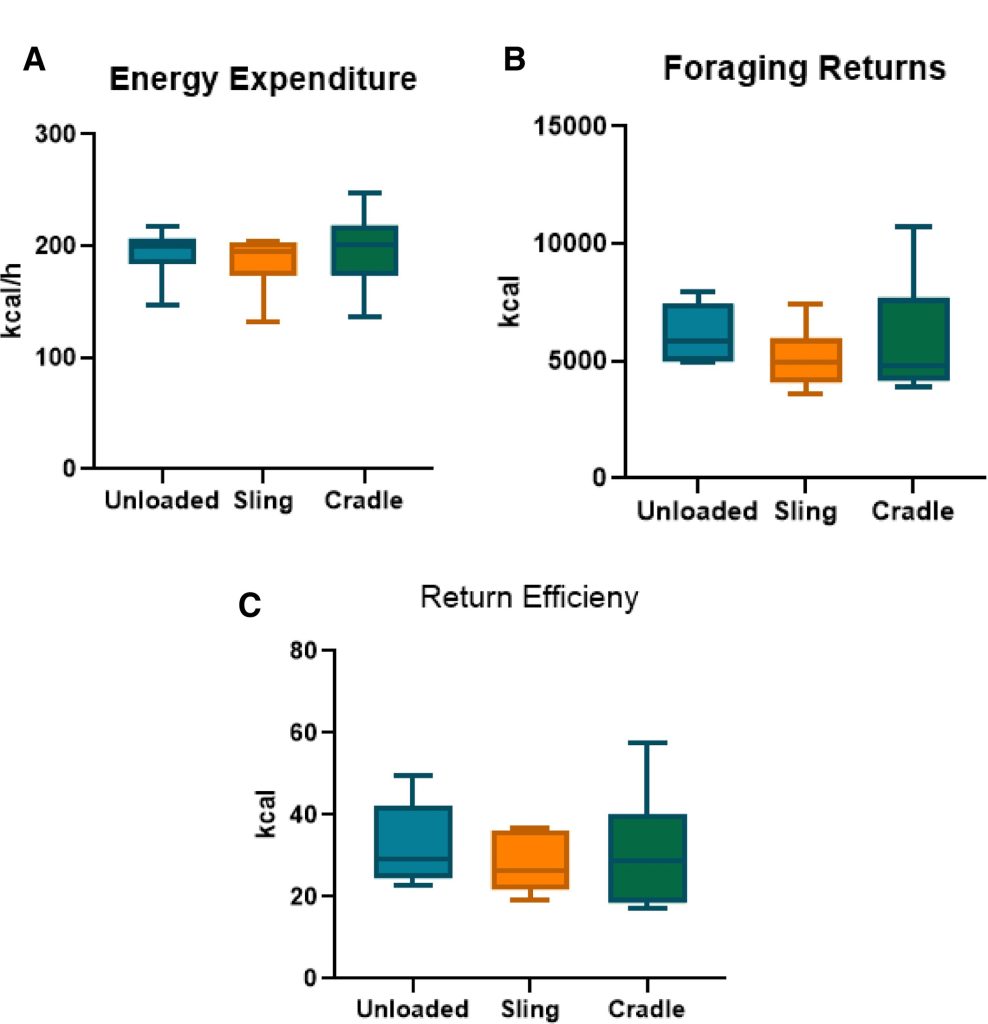
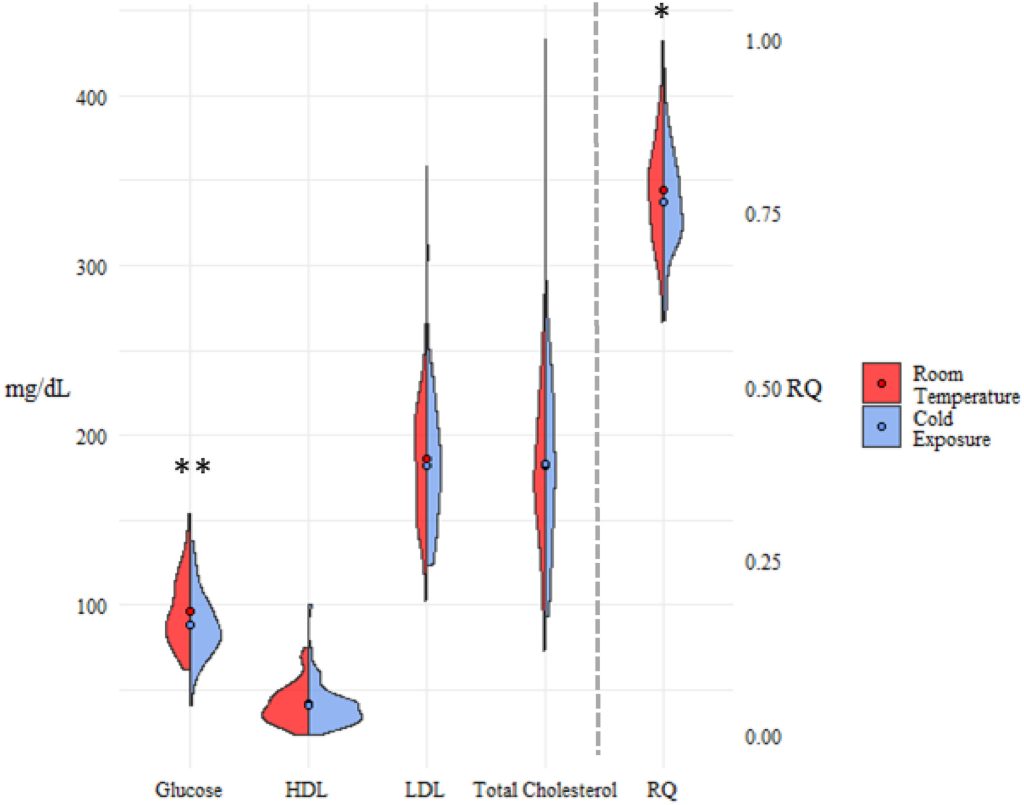
We have a new publication out in the American Journal of Human Biology looking at the relationship between resting metabolic rate and thyroid hormones (TSH, fT3, and fT4) among reindeer herders and office workers in Northern Finland. It is open access and can be found here.
We found that female reindeer herders exhibit a pattern different from all other participants in this study such that they had higher than expected RMRs, significantly higher free T3 and TSH, and a positive correlation between free T4 and RMR.
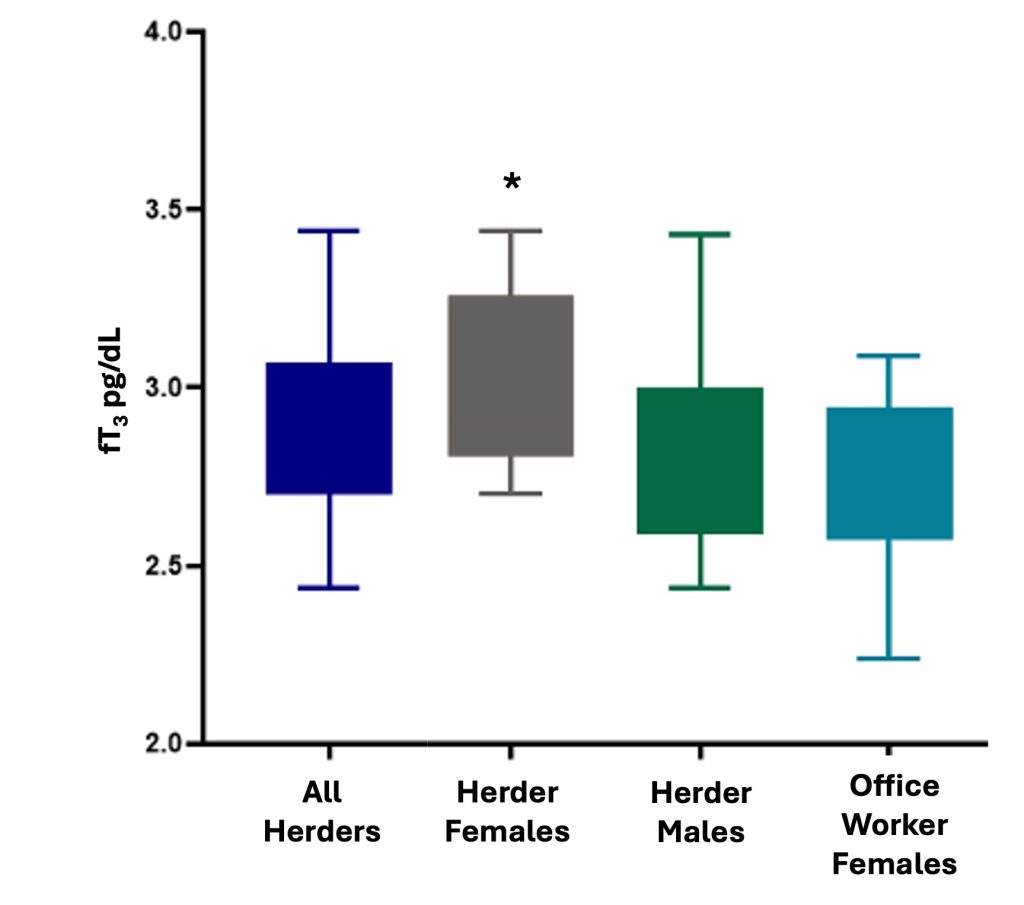
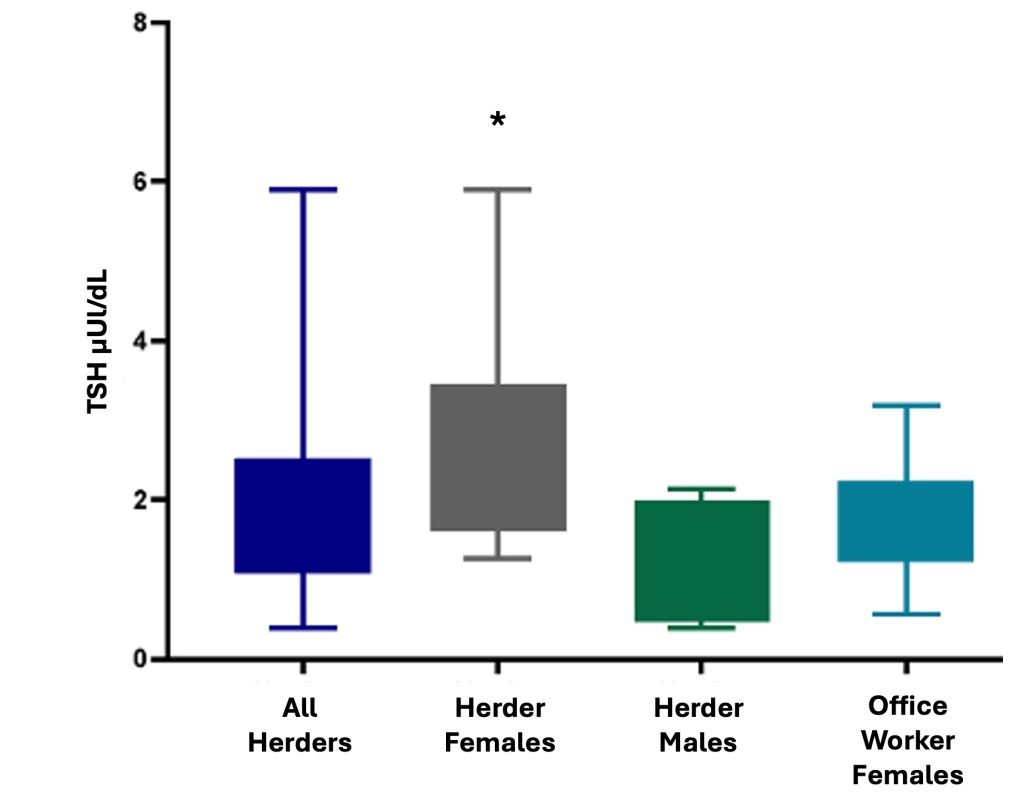
These results demonstrate that female reindeer herders are remaining physiologically resilient, potentially to protect reproductive capacity, in response to a drastically warming climate. We are also potentially witnessing a transition among male reindeer herders who are physiologically responding to the rapidly warming climate, as demonstrated by their highly variable RMRs. Finally, this work highlights the complex interaction between THs and the environment as demonstrated by the numerous environmental inputs (temperature, climate change, selenium levels, and local policy) experienced by the participants in this study. Future work will examine seasonal differences in RMR and TH dynamics as well as the impact of the menstrual cycle among herders and office workers providing greater insight into cold climate physiology and the metabolic response to climate change.