OpenRefine and the Distant Reader
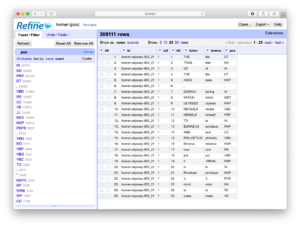
Posted on February 10, 2020 in Distant ReaderThe student, researcher, or scholar can use OpenRefine to open one or more different types of delimited files. OpenRefine will then parse the file(s) into fields. It can makes many things easy such as finding/replacing, faceting (think “grouping”), filtering (think “searching”), sorting, clustering (think “normalizing/cleannig”), counting & tabulating, and finally, exporting data. OpenRefine is an excellent go-between when spreadsheets fail and full-blown databases are too hard to use. OpenRefine eats delimited files for lunch.
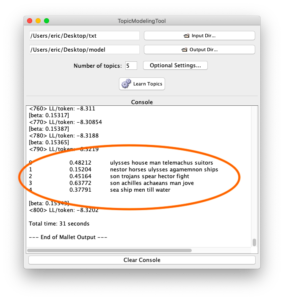
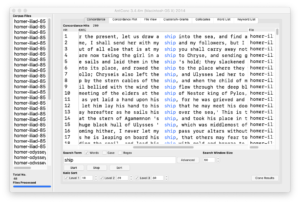
Many (actually, most) of the files in a study carrel are tab-delimited files, and they will import into OpenRefine with ease. For example, after all a carrel’s part-of-speech (pos) files are imported into OpenRefine, the student, researcher, or scholar can very easily count, tabulate, search (filter), and facet on nouns, verbs, adjectives, etc. If the named entities files (ent) are imported, then it is easy to see what types of entities exist and who might be the people mentioned in the carrel:
OpenRefine recipes
Like everything else, using OpenRefine requires practice. The problem to solve is not so much learning how to use OpenRefine. Instead, the problem to solve is to ask and answer interesting questions. That said, the student, researcher, or scholar will want to sort the data, search/filter the data, and compare pieces of the data to other pieces to articulate possible relationships. The following recipes endeavor to demonstrate some such tasks. The first is to simply facet (count & tabulate) on parts-of-speech files:
- Download, install, and run OpenRefine
- Create a new project and as input, randomly chose any file from a study carrel’s part-of-speech (pos) directory
- Continue to accept the defaults, and continue with “Create Project »”; the result ought to be a spreadsheet-like interface
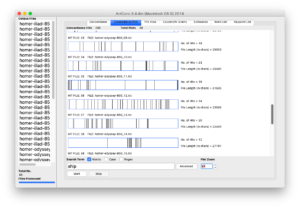
- Click the arrow next to the POS column and select Facet/Text facet from the resulting menu; the result ought to be a new window containing a column of words and a column of frequencies — counts & tabulations of each type of part-of-speech in the file
- Go to Step #4, until you get tired, but this time facet by other values
Faceting is a whole like like “grouping” in the world of relational databases. Faceting alphabetically sorts a list and then counts the number of times each item appears in the list. Different types of works have different parts-of-speech ratios. For example, it is not uncommon for there to be a preponderance of past-tense verbs stories. Counts & tabulations of personal pronouns as well as proper nouns give senses of genders. A more in-depth faceting against adjectives allude to sentiment.
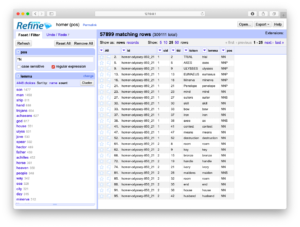
This recipe outlines how to filter (“search”):
- Click the “Remove All” button, if it exists; this ought to reset your view of the data
- Click the arrow next to the “token” column and select “Text filter” from the resulting menu
- In your mind, think of a word of interest, and enter it into the resulting search box
- Take notice of how the content in the spreadsheet view changes
- Go to Step #3 until you get tired
- Click the “Remove All” button to reset the view
- Text filter on the “token” column but search for “^N” (which is code for any noun) and make sure the “regular expression” check box is… checked
- Text facet on the “lemma” column; the result ought to be a count & tabulation of all the nouns
- Go to Step #6, but this time search for “^V” or “^J”, which are the codes for any verb or any adjective, respectively
By combining the functionalities of faceting and filtering the student, researcher, or scholar can investigate the original content more deeply or at least in different ways. The use of OpenRefine in this way is akin to leafing through book or a back-of-the-book index. As patterns & anomalies present themselves, they can be followed up more thoroughly through the use of a concordance and literally see the patterns & anomalies in context.
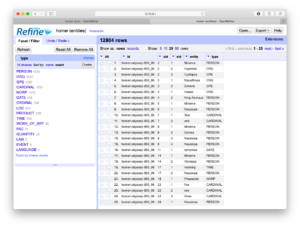
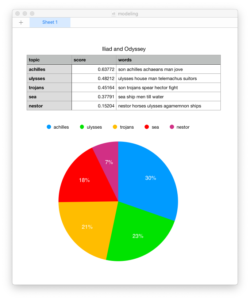
This recipe answers the question, “Who is mentioned in a corpus, and how often?“:
- Download, install, and run OpenRefine
- Create a new project and as input, select all of the files in the named-entity (ent) directory
- Continue to accept the defaults, but remember, all the almost all of the files in a study carrel are tab-delimited files, so remember to import them as “CSV / TSV / separator-based files”, not Excel files
- Continue to accept the defaults, and continue with “Create Project »”; the result ought to be a spreadsheet-like interface
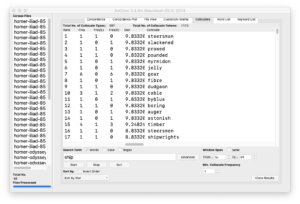
- Click the arrow next to “type” column and select Facet/Text facet from the resulting menu; the result ought to be a new window containing a column of words and a column of frequencies — counts & tabulations of each type of named-entity in the whole of the study carrel
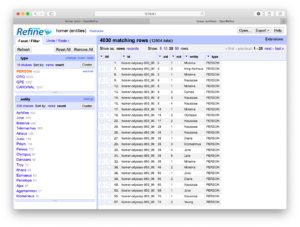
- Select “PERSON” from the list of named entities; the result ought to be a count & tabulation of the names of the people mentioned in the whole of the study carrel
- Go to Step #5 until tired, but each time select a different named-entity value
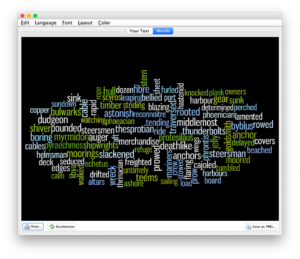
This final recipe is a visualization:
- Create a new parts-of-speech or named-entity project
- Create any sort of meaningful set of faceted results
- Select the “choices” link; the result ought to be a text area containing the counts & tabulation
- Copy the whole of the resulting text area
- Paste the result into your text editor, find all tab characters and change them to colons (:), copy the whole of the resulting text
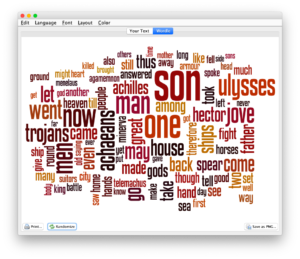
- Open Wordle and create a word cloud with the contents of your clipboard; word counts may only illustrate frequencies, but sometimes the frequencies are preponderance.
A study carrel’s parts-of-speech (pos) and named-entities (ent) files enumerate each and every word or named-entity in each and every sentence of each and every item in the study carrel. Given a question relatively quantitative in nature and pertaining to parts-of-speech or named-entities, the pos and ent files are likely to be able to address the question. The pos and ent files are tab-delimited files, and OpenRefine is a very good tool for reading and analyzing such files. It does much more than was outlined here, but enumerating them here is beyond scope. Such is left up to the… reader.