by Greg Bond, Sports Archivist and Curator, Joyce Sports Research Collection
The 1972 Official Program for the Toledo Troopers football team introduced the squad to readers by reprinting a local newspaper story about two reporters watching a typical practice:
What seemed so incomprehensible about it all was what they were hearing and seeing was no ordinary football team. There were some telltale signs, such as a pigtail here and there, a high-pitched shout or two, maybe a trace of lipstick on a jersey sleeve; and once the helmets came off, there was no mistaking… these were girls, women who at first glance seemed so removed from the kitchen, so totally removed from all the things that the so-called “weaker sex” usually does.
The 1972 Troopers program is part of a small recently acquired National Women’s Football League (NWFL) Collection that documents the history of the NWFL and the history of women’s professional football. The Troopers, one of the earliest—and the most successful—professional women’s tackle football teams in the country, first took the field in 1971 and were a founding member of the National Women’s Football League in 1974.
Women’s football was part of the larger women’s sports revolution of the 1960s and 1970s that both came before and was fueled by Title IX legislation in 1972. Despite the changing social mores, women football players still frequently encountered discrimination, stereotypes, and skepticism—even from sympathetic observers like the reporters in Toledo. Nevertheless, women’s football carved out a following. During the heyday of the National Women’s Football League in the mid-1970s, games attracted thousands of fans.
The new collection documents both the NWFL and an earlier barnstorming period when the best women’s football teams played irregular schedules with few formal league structures. A 1972 New York Fillies vs. Midwest Cowgirls scorecard is representative of the pre-NWFL material.

In 1974, the National Women’s Football League regularized competition between the top women’s football teams and stretched from Ohio to Texas to California. The new league attracted increased attention and provided stability to the sport for several seasons. The NWFL collection contains several game programs and yearbooks from teams like the Toledo Troopers and the Detroit Demons.


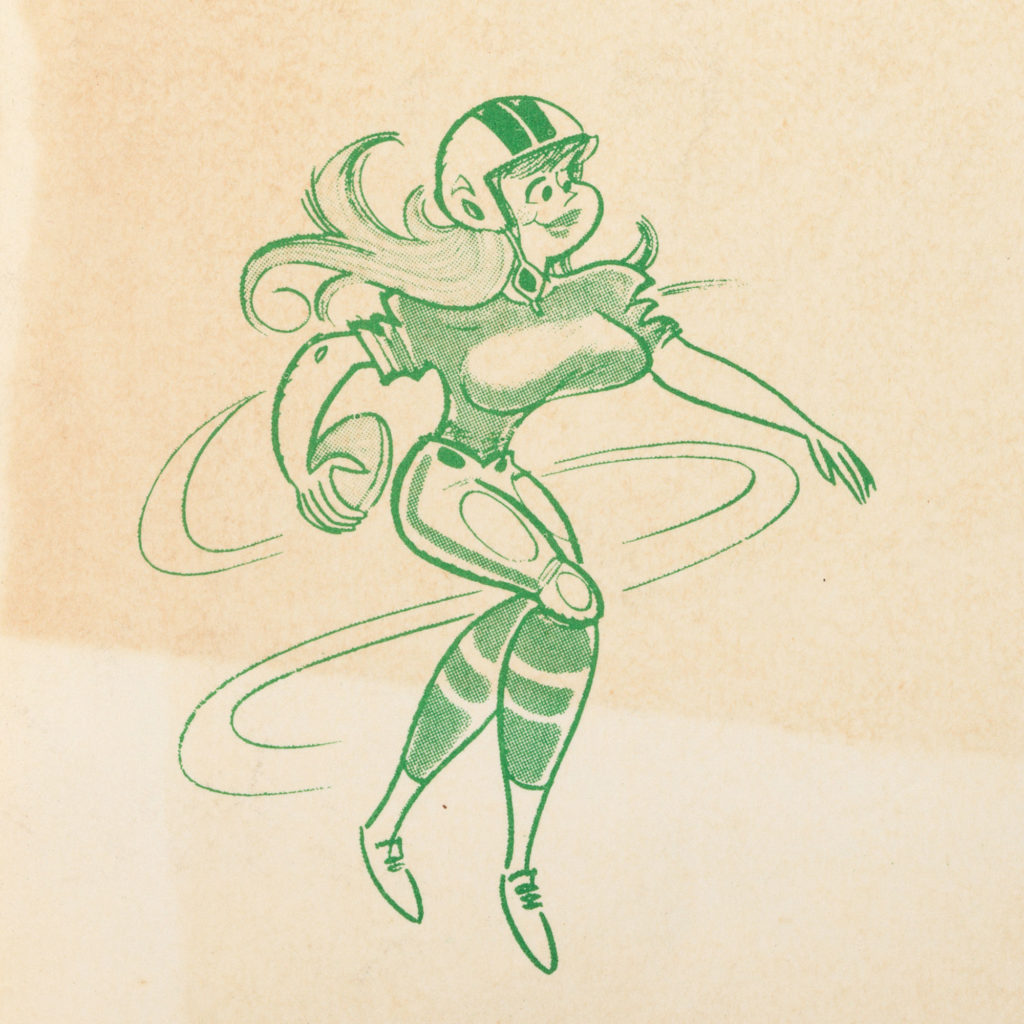
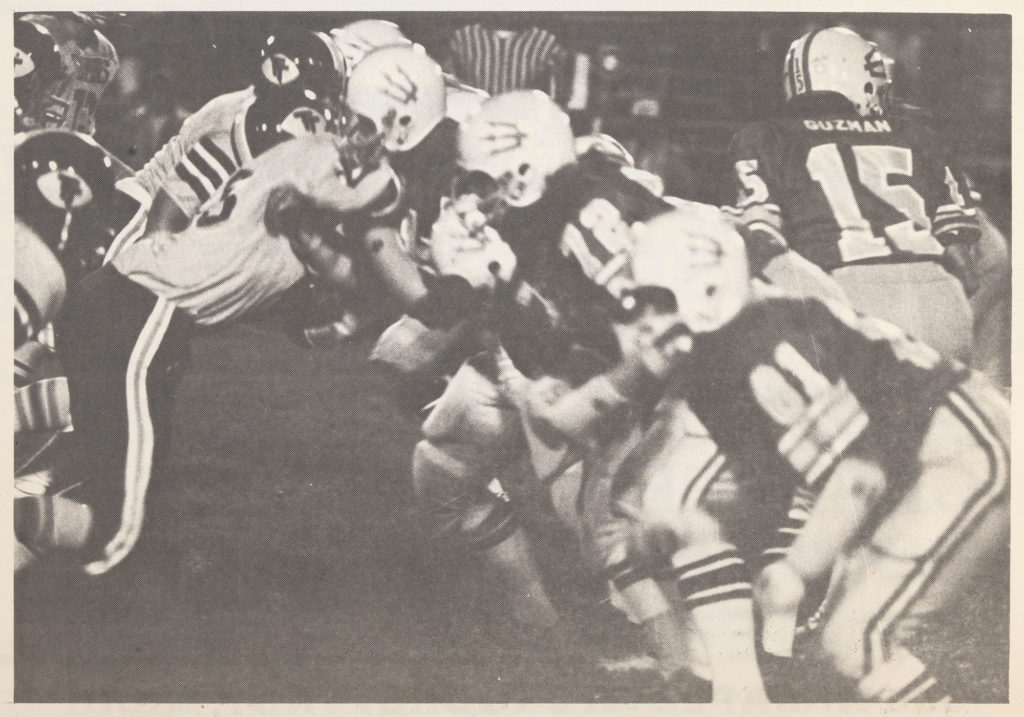
Some representations of women’s football players in these publications, like the cartoon below from the 1972 New York Fillies scorecard, relied on stereotypes and sex appeal. But most images in NWFL publications showcased the athletes’ football skills as seen in these pictures of Troopers and Demons players in game action and in practice .



Financial difficulties, long travel distances, and declining attendance, however, forced several of the NWFL’s best teams, including the Toledo Troopers, to go out of business after the 1979 season. By the early 1980s, the National Women’s Football League only had franchises in the states of Michigan and Ohio. The league ceased operations in 1988.

To read more about the history of women’s football, see: Hail Mary: The Rise and Fall of the National Women’s Football League by Britni De La Cretaz and Lyndsey D’Arcangelo; and We Are the Troopers: The Women of the Winningest Team in Pro Football History, by Stephen Guinan. Both of these titles are available at Hesburgh Libraries.
The National Women’s Football League Collection is open and available to researchers. We also welcome additional donations of material that document the history of women’s professional football.