If the majority of Late Antique Europeans living in the former Roman territories were, at the very least, nominally Christian in the eighth century CE, what was the religion of the peoples of Late Antique North Africa, Rome’s southern lands during the same period?
Given that the region of North Africa — the lands from what is today western Morocco to Egypt– gave the Christian world some of its earliest texts, had more bishoprics than other regions, and was the home of St. Augustine, one of the four doctors of the Catholic Church, it stands to reason that this region was quite Christian in the year 700.

Yet until recently, this argument was not advanced by scholars of Late Antiquity, the European Middle Ages, or Islamic History. If anything, North Africa c. 700 was seen as nominally Muslim, due in large part to the Arab conquests of 670-710. In fact, so few scholars discussed the idea of Christians in North Africa that, as recently as 2004, an article pointing to proof of Christian communities in North Africa post Arab conquest was described by one reviewer as “pull[ing] the rug out from under the feet” of naysayers.
Now, it seems that more scholars are pointing towards the continuation of Christianity in North Africa c. 700, with some even going as far as to point to evidence of Christian communities in the twelfth century. However, this group is still quite small, and the wide range of territory, both geographical and historical, that a potential researcher must cover is immense, to say nothing of the required linguistic skills in Medieval Latin, Ancient Greek, and now, Arabic, required to decipher extant evidence.

Yet what about the Muslim conquests? How did this event shape the religious landscape of North Africa between 700 and 800 CE?
For one thing, it seems as though the Muslim conquests brought about the conversion of the Amazigh (Berbers), who, despite putting up several decades of resistance to the Arab invaders, accepted the new faith with gusto. Having attached themselves to their new Arab overlords as their mawali —a status that indicated conversion to Islam and affiliation with an Arab tribe–these new converts joined the Umayyad armies in Qayrawan and participated in the conquest of the Iberian peninsula, both as generals and as settlers.
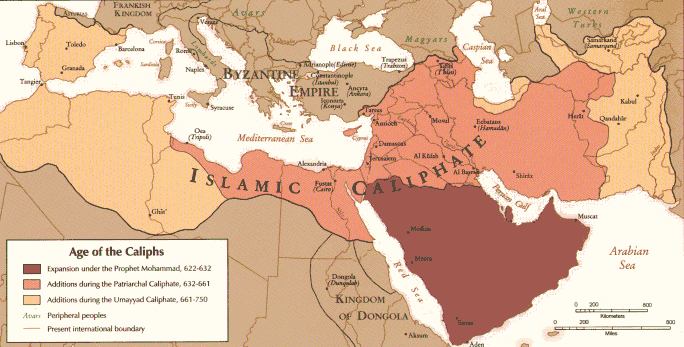
So quick was this conversion that come 740, the Amazigh were already fully enmeshed in Arab-centric quarrels on the question of who, exactly, should be God’s deputy (khalifat Allah) and lead the faithful during this life and the next. Although there had been periods of unrest in the preceding decades, in 740 the Muslim Amazigh rebelled against the Umayyad caliphs under the banner of Kharjism, an Islamic sect that had, since c. 658 rejected both the ruling Umayyad caliphs and the Shi’a ‘Ali as God’s correct deputy. This “Berber Revolt” successfully divorced the regions of North Africa west of Egypt from the Umayyad caliphate in 744, leading to the growth of the first independent and autonomous Islamic dynasties.
Thus, circa 700, there appears to be a Late Antique African Christian population that is either somehow subsumed under a Muslim population by 740 due to mass conversion of the Amazigh to Islam; or exists side by side with their new Muslim brethren for centuries but, due to the fact that independence from the Islamic caliphate was gained under the banner of Islam and not Christianity, were “lost” to history until now.
A third possibility exists, however, namely that both of these pictures of North Africa and its confessional affiliations are only partially true and need to be amended in order to reflect what was actually going on in the region between. It is this path that will be explored in subsequents posts.
A.L. Castonguay
Ph.D. Student
Department of History
University of Notre Dame
References
- Khalid Yayha Blankinship. The End of the Jihād State. The Reign of Hishām ibn ‘Abd al-Malīk and the Collapse of the Umayyads. Albany: SUNY Press, 1994.
- Mark A. Handly. “Disputing the End of African Christianity,” in A.H. Merrills (ed.), Vandals, Romans, and Berbers. New Perspectives on Late Antique North Africa. Aldershot: Ashgate, 2004: 291-310
- Anna Leone. “Bishops and Territory: The Case of Late Roman and Byzantine North Africa,” Dumbarton Oaks Papers, Vol. 65/66 (2011-2012): 5-27
- R.A. Markus. “Review: Vandals, Romans, and Berbers. New Perspectives on Late Antique North Africa by A.H. Merrills,” The English Historical Review, Vol. 120, No. 487 (Jun., 2005): 759-760
