Recently, I composed a blog on my role as playwright, academic consultant and creative & theatrical director of two recent Renaissance faires, and I then followed up with a blog centered on the community spirit that imbued our first faire, Wyndonshire Renaissance Faire. This blog will take the second of our inaugural 2024 spring faires, Enchanted Orchard Renaissance Faire, as the topic of discussion, and continue discussion of the community efforts that went into putting this event together at warp speed. In addition, I will discuss the educational and agricultural focus of this faire, which brought regional tourism to North Central Massachusetts and offered the opportunity to create a story that explores issues specific to local and sustainable farming. This year, Enchanted Orchard will commence in just a few weeks, on May 3rd and 4th 2025.

As I mention in my previous blog, after building the creative team at Wyndonshire, because of some uncertainty with respect to funding the project by the town of Winchendon, my wife, Rajuli, and I reached out to a local farm and festival venue, Red Apple Farm, owned by Al and Nancy Rose, to see if they might be open to bringing a Renaissance Faire to their business in the event that we needed a change of venue. After pitching the project, the whole team at Red Apple Farm was excited for the prospect, and once Winchendon determined they were able to move forward with the project, we agreed to produce a second “sister” faire with Red Apple Farm, with characters and plot lines intersecting with those at Wyndonshire. I began to conceive of a second fantasy realm, the agrarian kingdom of Enchanted Orchard.

Rajuli’s and my ability to produce a second large-scale Renaissance Faire was only possible with the help of our team, what became FaeGuild Wonders, and Red Apple Farm, our incredible partnering venue. Red Apple Farm embraced our vision and helped shape and grow Enchanted Orchard into the fabulous event that it was, ranked by a popular vlogger, Chelle Belle, as one of the best Renaissance Faires in New England last year (2024). Al and Nancy Rose, the entrepreneurial owners behind the blooming success of Red Apple Farm, are some of the kindest and most collaborative people I’ve personally had the chance to partner with, and without their leadership, there would be no Enchanted Orchard (and for that matter, no NorthFolk Nightmarket). They partner with local businesses, and are committed to growing regional tourism and community, which is deeply embedded in their mission and the way they run their business.

In addition to Al and Nancy Rose, our Orchard Stewards, Enchanted Orchard thrived because of many other members of the Red Apple Farm team, including Sarah McLennan (who coordinated vendors and helped organize the event), Kirsten Killay (who manages the Red Apple Farm Cidery), Loryn Killay (who spearheads marketing and promotion necessary to advertise the event), Aaron Rose (who redesigned the webpage) and the Sams—Samuel Miller and Samuel Dosset—who constructed the picturesque towering gate that leads into the fantasy kingdom of Enchanted Orchard. The latter Samuel updated the event’s map to account for the faire’s expansion this year, and has become Enchanted Orchard’s royal cartographer.

To further highlight the level of Red Apple Farm’s integration into the event, their Cidery—transformed into the Toadstool Tavern for Enchanted Orchard—featured all the different flavors made specifically for the faire. Many of these ciders developed for the event are now standard or seasonal options available throughout the year at Red Apple Farm’s Cidery. Moreover, the cider is a connecting point for our events, as it is one of the main economic exports of the Enchanted Orchard kingdom, and it was available at Wyndonshire as well as an imported drink from their neighboring kingdom.

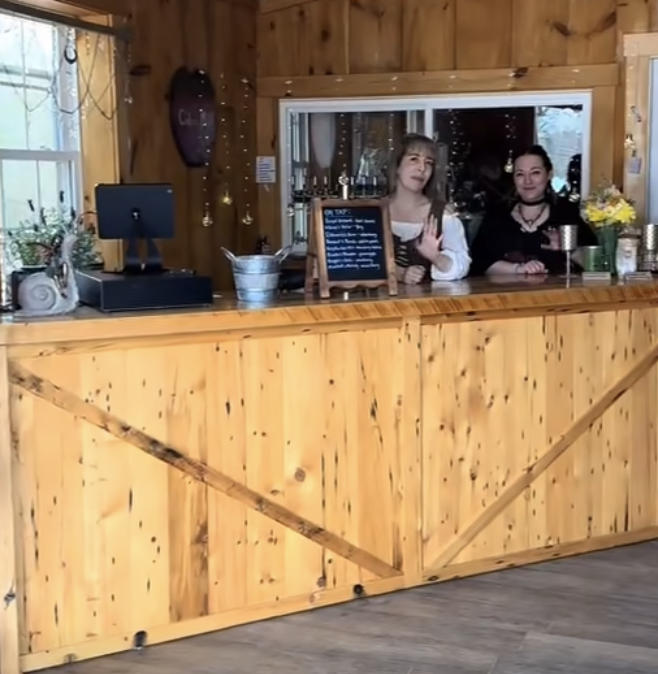
Red Apple Farm also collaborates with a local restaurant, the Gardner Ale House, which manages the Brew Barn at Red Apple Farm. The Brew Barn is a cozy, tavernesque restaurant on the farm, which serves food and drink, and was crucial for the success of Enchanted Orchard’s second day (Sunday, May 5th, 2024) when the rain threatened to drown out the event. Because of the Brew Barn’s openness to collaborating, we were able to pivot and move many performance acts inside and out of the inclement weather. Although this required a major reworking of the schedule, we did our best to make sure each performer or group had at least one indoor show in case they were rained out during their showtime. While the rain did put a damper on some performances, the event was sustained by adding outdoor fires throughout the faire and bringing many of the performances indoors and the event was a success. Despite the weather, the turnout and experience from patrons on the second day was extremely positive and this gave us the added benefit of a learning opportunity with respect to what to plan for in the case of inclement weather in future.
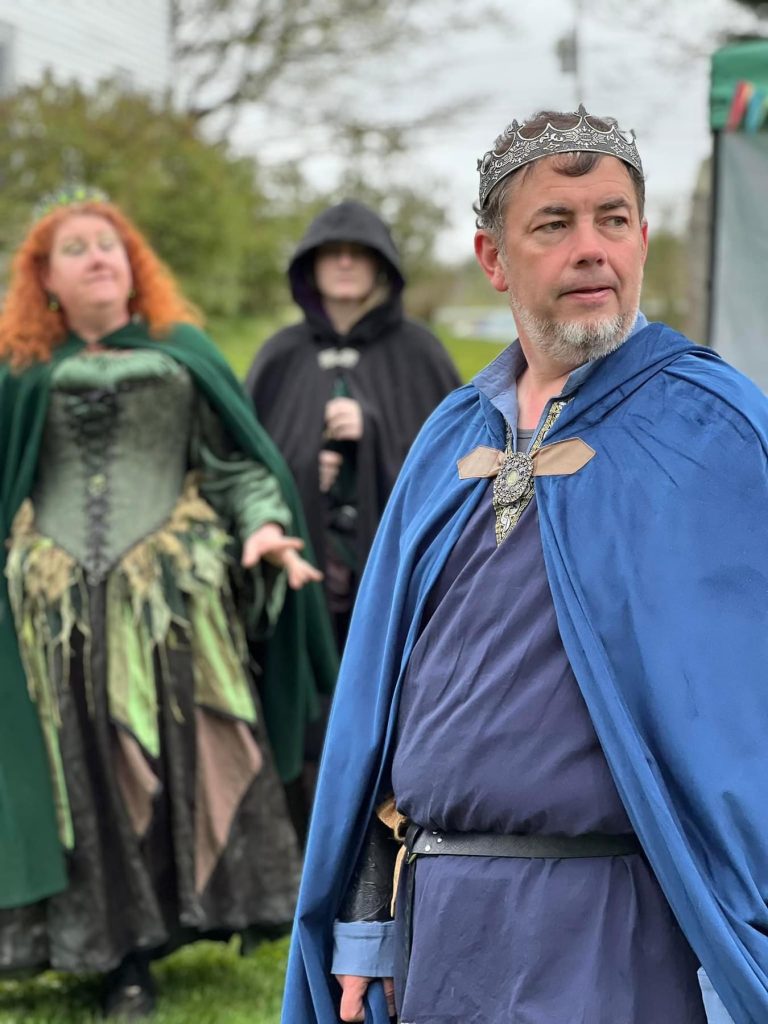

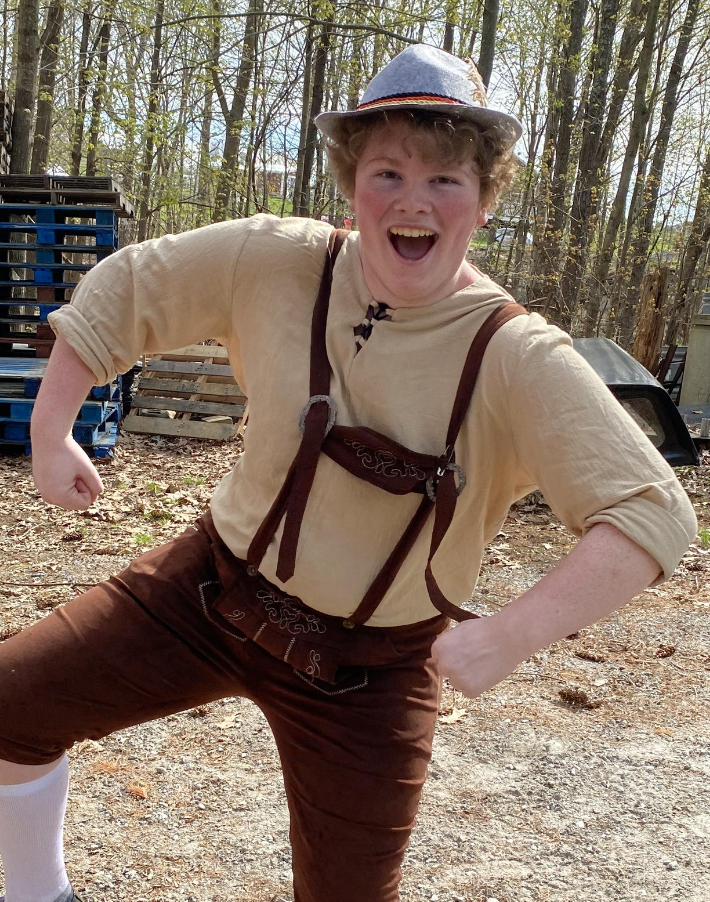
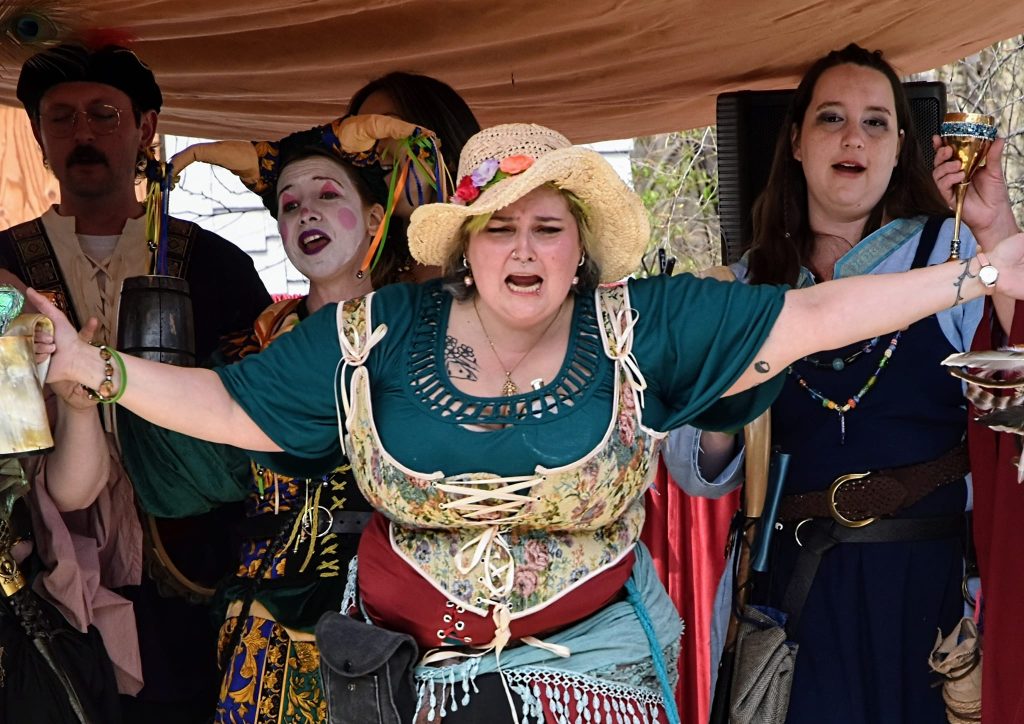
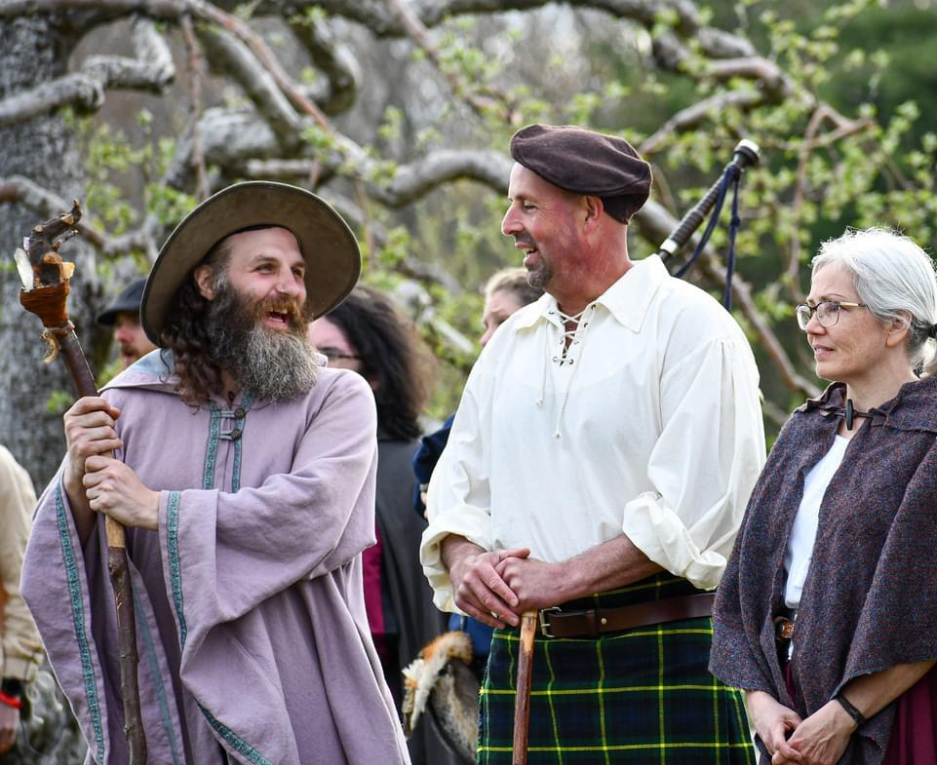
I wrote an entirely new script for this faire, and last year’s story, “Seeds of Wonder,” was a prologue to the first act, “The Romance of the Orchard,” which will commence this year. Enchanted Orchard Renaissance Faire highlights sustainable farming which was the foundation of agrarian life in the medieval world. The major conflict in this faire centers on the issue of conservation versus preservation. This takes the form of a heated debate between the Enchant Orchard nobility with the May Queen (played by Tammy Dykstra and Siobhan Doherty) and Duke of Thorns (played by Dave Fournier) arguing for the protection of the Thornwood and the creatures that live there, who are part of the kingdom’s broader ecosystem. Alternatively, the Orchard King (played by Paul Taft and Gary Joiner) and Blossom Baroness (played by Jen Knight) contend that expanding the orchard would better provide for the people of the kingdom and foster economic growth for the realm while at the same time minimizing food insecurity throughout the kingdom. This tension is played out in both staged theatrical scenes and numerous immersive skits and side conversations had between members of the Enchanted Orchard nobility throughout the event.
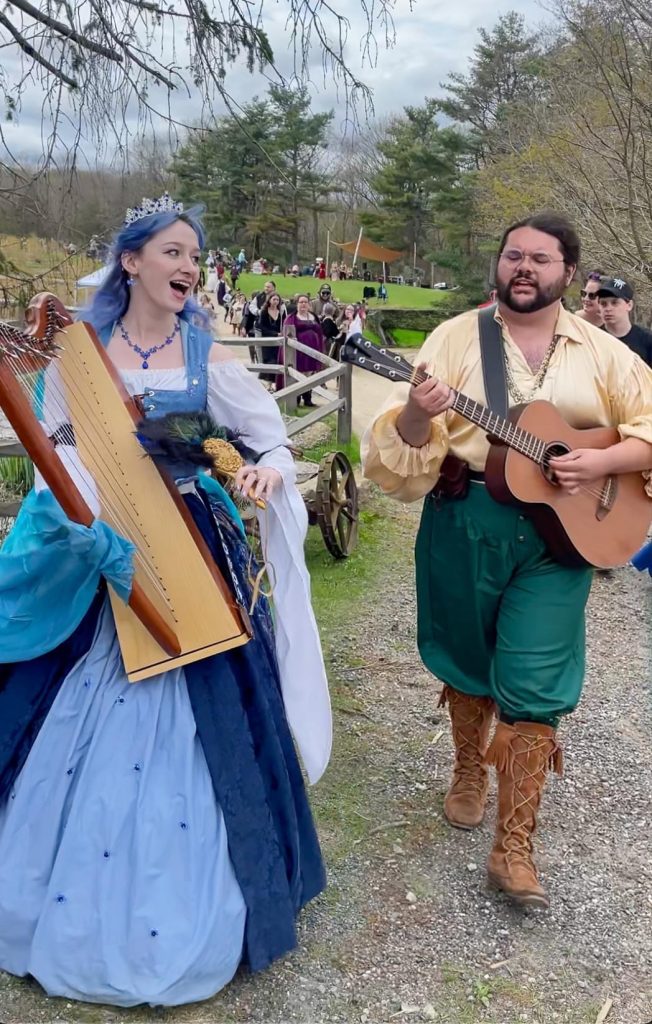

Toward this end, the Orchard King takes advantage of his royal authority to press upon the newly returned Prince of Leaves (played by Michael Barboza-McLean and Vajra Spring), advocating for the virtues of his proposed expansion of the orchard. Because the Prince of Leaves seems somewhat amenable to his ideas and influence, and seizing an opportunity to undercut the wishes of his rival, the May Queen, the Orchard King announces at the end of Enchanted Orchard’s annual Beltane Banquet, that he is betrothing his daughter, Blueberry Princess (Melanie “Melegie” Long), much to her sorrow and surprise, to his rival’s son, the Prince of Leaves, in an effort to “weave peace” in the realm and as a means to press his advantage on the young prince now enfianced to the heiress of the realm.
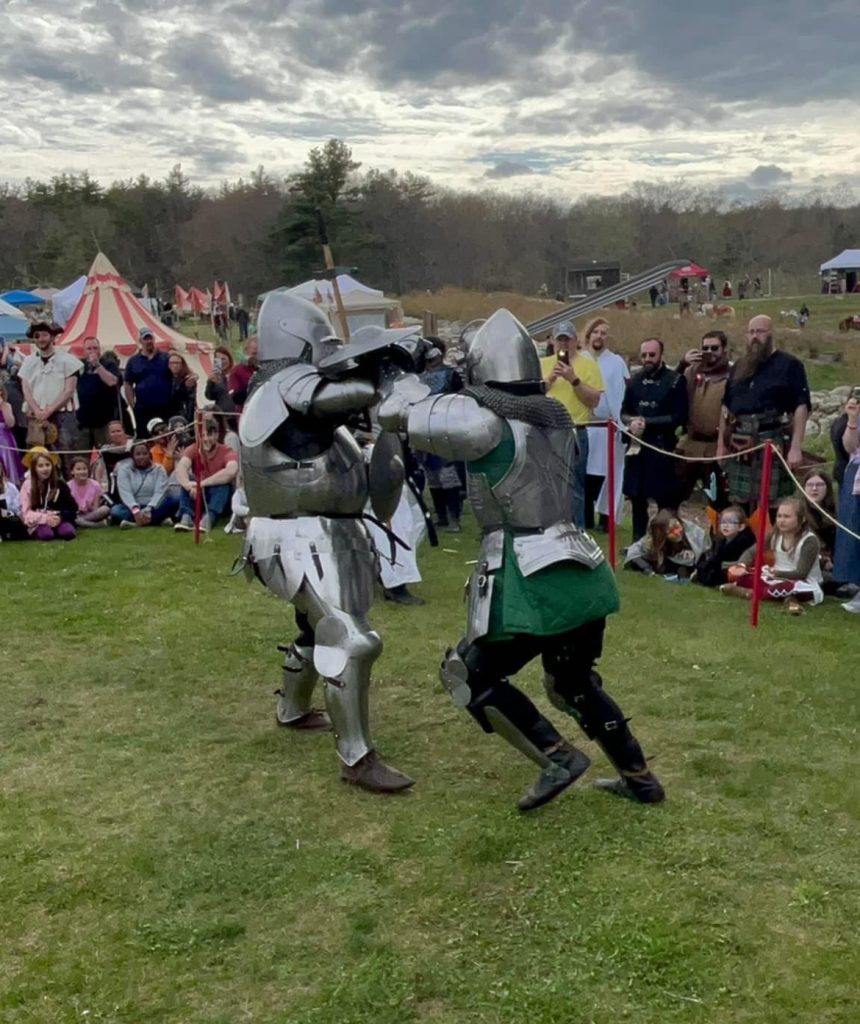

However, because of the fast production of this faire, the script was centered primarily on the nobility, leaving many of the other characters to participate in a highly immersive and interactive character scavenger hunt, which invited patrons to find and receive specific items from cast members in order to earn a small prize. This encouraged frequent interaction between character actors and patrons, and the activity was a huge success, especially with the kinderfolk who attend. The scavenger hunt was coupled with a “knight’s quest”, which asked patrons to find a noble from each house and resulted in a knighting ceremony, conducted by the royal champions from the The Knights of Lord Talbot. Moreover, the Sheriff of Thornwood (played by Jennifer MacLean), gave out citations through the day to fairgoers for various offenses and Sir John Fastolf (Frank Walker) held a baronial court to deal out justice for crimes cited by the Sheriff, which might sometimes involve a short stay in the stockades.
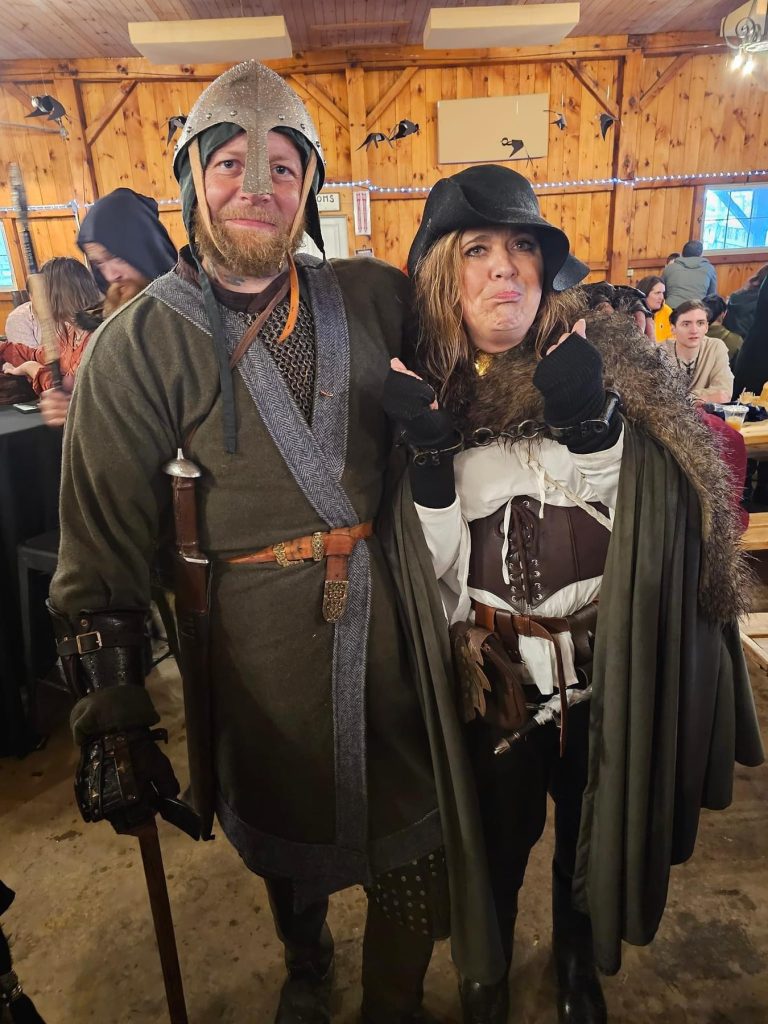

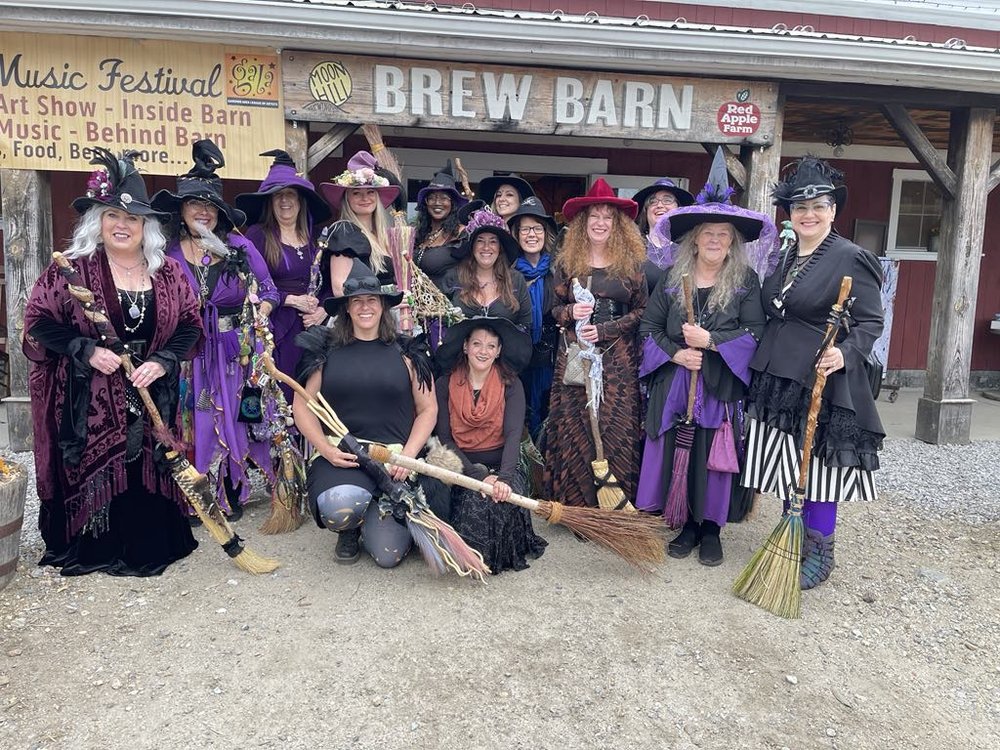
As with Wyndonshire, The Green Sash marauders raided Orchard Toward, while the The Mt. Wichusett Witches made secret bargains and brewed magic potions for a number of the Enchanted Orchard nobles, ending with a flash mob dance that led patrons to the final event at the faire, the community Maypole dance which brought performers, cast members and patrons together for a final celebration of spring and the planting season.
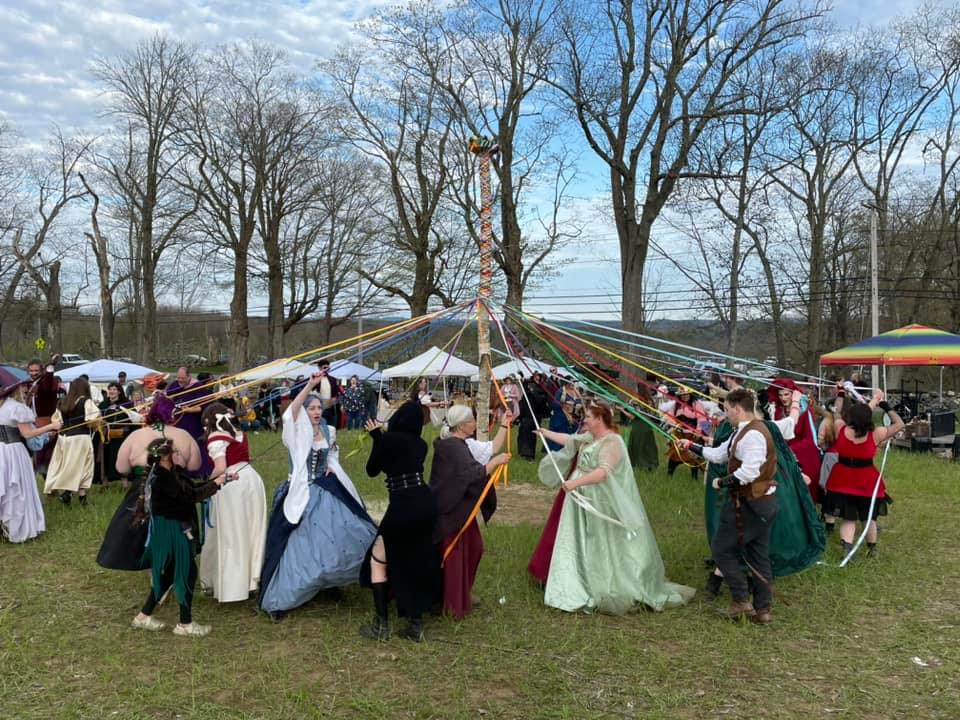

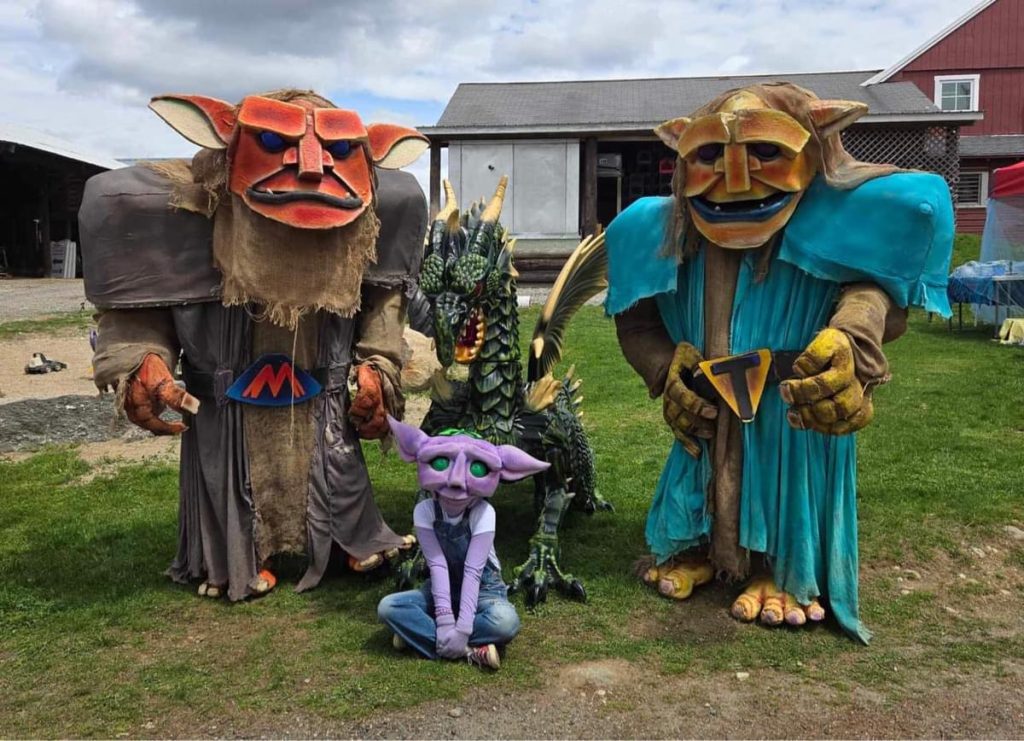
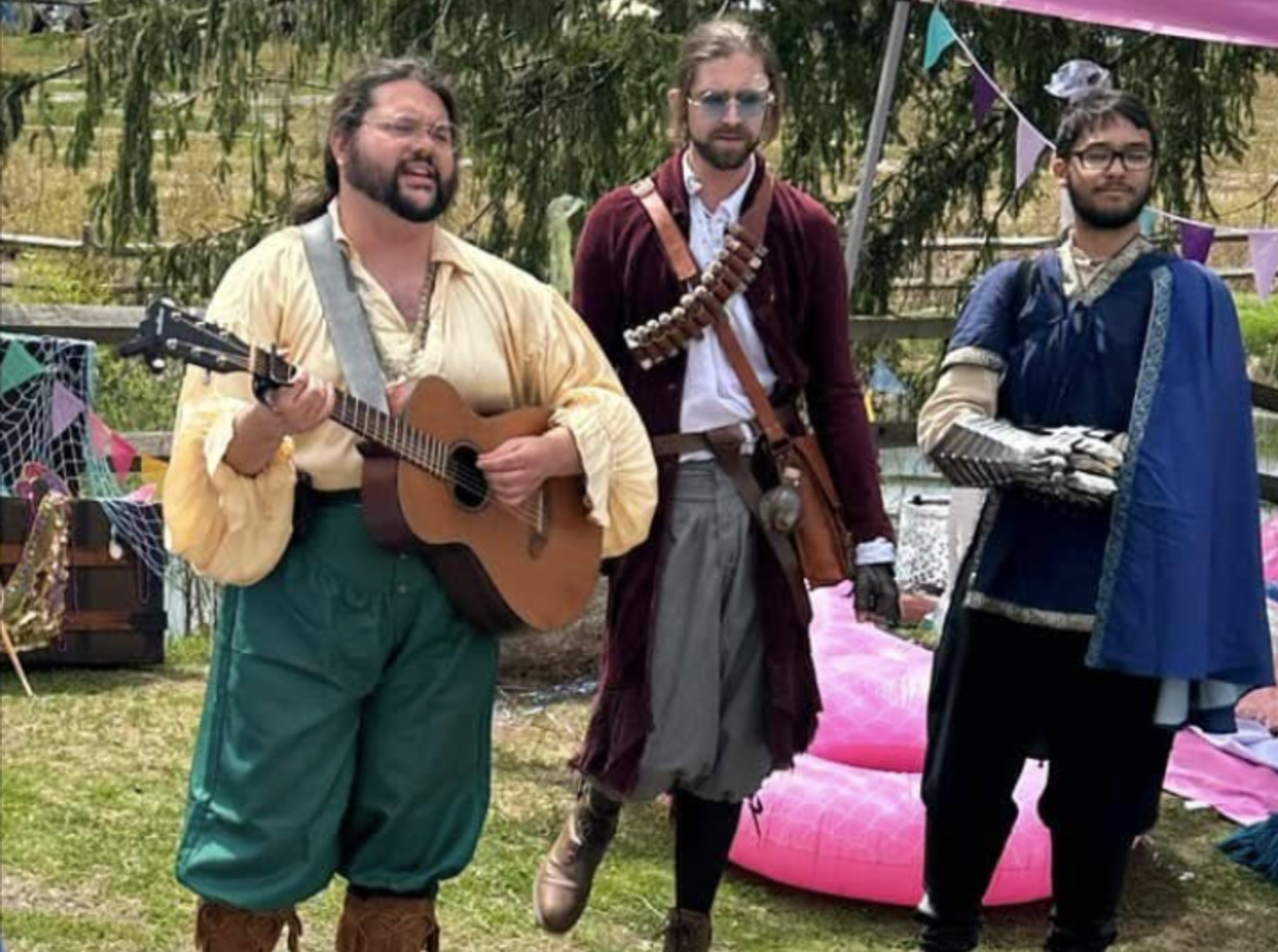
Some of the theatrical performance groups were familiar from Wyndonshire: such as the The Phoenix Swords, The Harlot Queens, The Warlock Wondershow and LaLoopna Hoops. Many musical groups were at both faires as well, namely Meraki Caravan, The Shank Painters, XPresso and Dead Gods are the New Gods. However, there were some new faces at Enchanted Orchard as well, such as Skeleton Crew Theater [giant troll-puppets], Diva Di [Shakespeare drag artist], Massachusetts Historical Swordsmanship [HEMA] [medieval European combat] and solo fire performers such as Samantha Lynne and Luna Faun. This year we welcome some additional performing groups, including the Iconic Sproutin’ Divas [featuring Diva Di and other drag artists], Winds of Alluria [musical group], Michael OJ [magician], Finlay’s Fire Troupe [fire-spinning show], and Captain Tactless [tavern musician], Dume & Glume: Ethical Executioneers [improv comedy show], The Misfits of Avalon [musical group], Bayt Al-Asad: House of the Lion [medieval Middle Eastern combat], and Combatant’s Keep [medieval joust show].
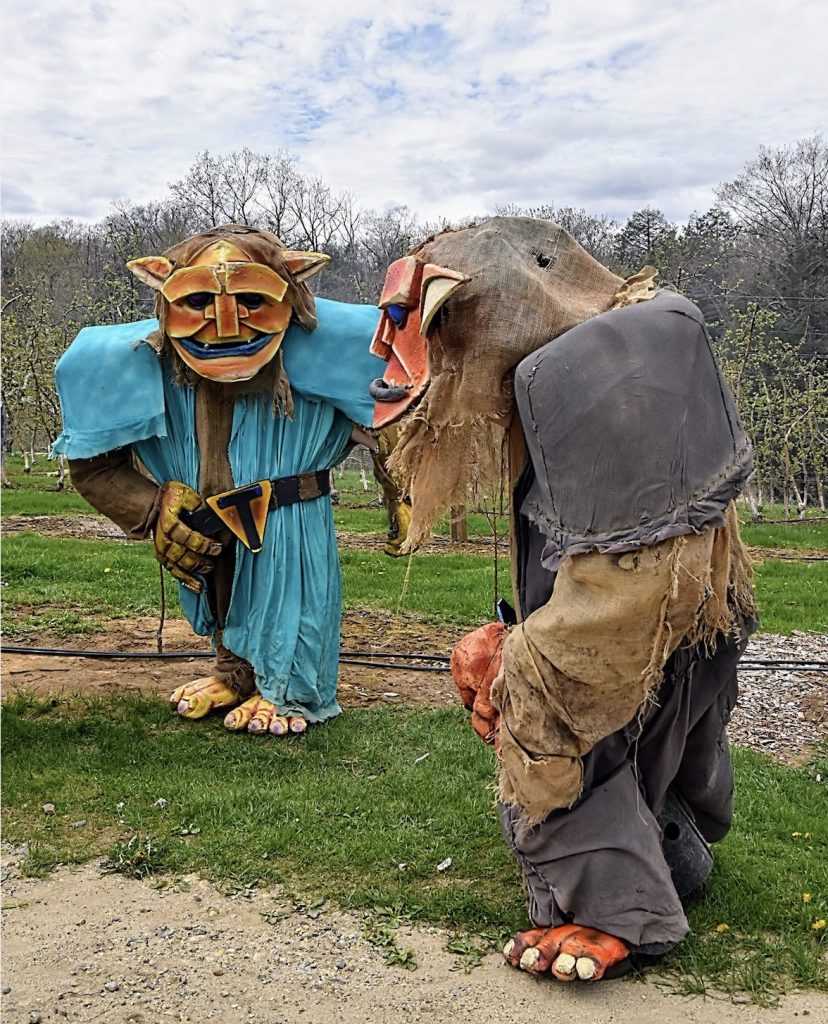

The Orchard King made a surprise wedding pronouncement arranging the union of his daughter, the Blueberry Princess, and the Prince of Leaves, the son of his rival, the May Queen, at the end of last year’s faire. Enchanted Orchard’s second annual event picks up where last year left off, and this year features “The Romance of the Orchard,” in which a love triangle blooms and whispers of revolution and news of “The Wyndonshire Wedding” and the fall of Wyndonshire spreads to all of high and low estate. If you came last year to experience the magic of our inaugural faire, we hope that you return for more wonders and delights. f you didn’t make it last year, and you enjoy immersive storytelling and modern medievalism, we hope you join us this year for Enchanted Orchard Renaissance Faire 2025—which brings together the local performing art and farming communities in North Central Massachusetts—and combines theater, music, comedy, performance art, interactive activities, family fun and an artisan vendor market.

Fairegoers will be able to learn how to sword fight, try their skill at axe-throwing, ride a unicorn or catch a goblin hayride, watch a joust and medieval melee combat in both European and Middle Eastern traditions. This year, Enchanted Orchard will commence on the first weekend in May, so consider saving the date, and I hope to see you there—just look for the wandering wizard!
Richard Fahey
PhD in English
Medieval Institute
University of Notre Dame
Creative & Theatrical Director
FaeGuild Wonders