Pilgrimage and the institutions that supported it spanned the many cultures and religions of the ancient and medieval worlds. It was a truly global phenomenon of the Middle Ages. Pilgrims undertook their journeys to fulfill religious obligations, to give thanks for healing, and to receive counsel from spiritual experts. Established routes led to sacred sites located on natural landmarks or along waterways, and marked by temples, shrines, churches and mosques. Often pilgrims desired contact with a sacred object, like an image of the divine, believed to possess healing power.
Going on pilgrimage still appeals today to people religiously affiliated or not, and medieval routes continue to attract travelers. Moreover, pilgrimage is now being used in justice work as an embodied practice that can support liberation and healing. What are the common threads and important differences between the practice of pilgrimage in the deep past and our present moment? Can the long history of pilgrimage inform current thinking about hospitality and encounter?
The imperative to provide hospitality catalyzed the invention of major social institutions in the Middle Ages. Hospitals and other charitable associations were established across Africa, Europe, and Asia to house pilgrims along their route and welcome them at their destination. On pilgrimage, medieval people encountered different cultures, and a rich literature developed as writers published accounts of their travels. Ibn Battuta, a Muslim jurist from Morocco, devotes much of his famous travel narrative to recounting visits with Sufi saints and Islamic scholars; as he made the obligatory pilgrimage to Mecca in 1325, he sought out their learning and their blessing. Similarly, the English Christian merchant and author Margery Kempe emphasizes the positive relationships she fostered while on pilgrimage to Jerusalem and Rome in 1413. She finds help and support from Muslim tour guides who comfort her, a German priest who hears her confession, and wealthy Italian women who provide for her when she embraces voluntary poverty. Pilgrimage, for these writers, was as much about the journey as the destination.
The Medieval Institute’s public humanities initiative for Spring 2023 will investigate pilgrimage as a global medieval phenomenon structured by practices of hospitality and cross-cultural encounter. Our “Pilgrimage for Healing and Liberation” will, first, educate the public about the history, theology and liberatory praxis of pilgrimage and, second, sponsor two pilgrimage experiences. These events will help all who participate to understand how histories of violence and inequity have shaped our local environment in South Bend and to imagine how we might create a more just and inclusive community through systemic transformation. The participatory nature of pilgrimage lends itself to the work of public humanities as we partner with community organizations to “learn by doing.”
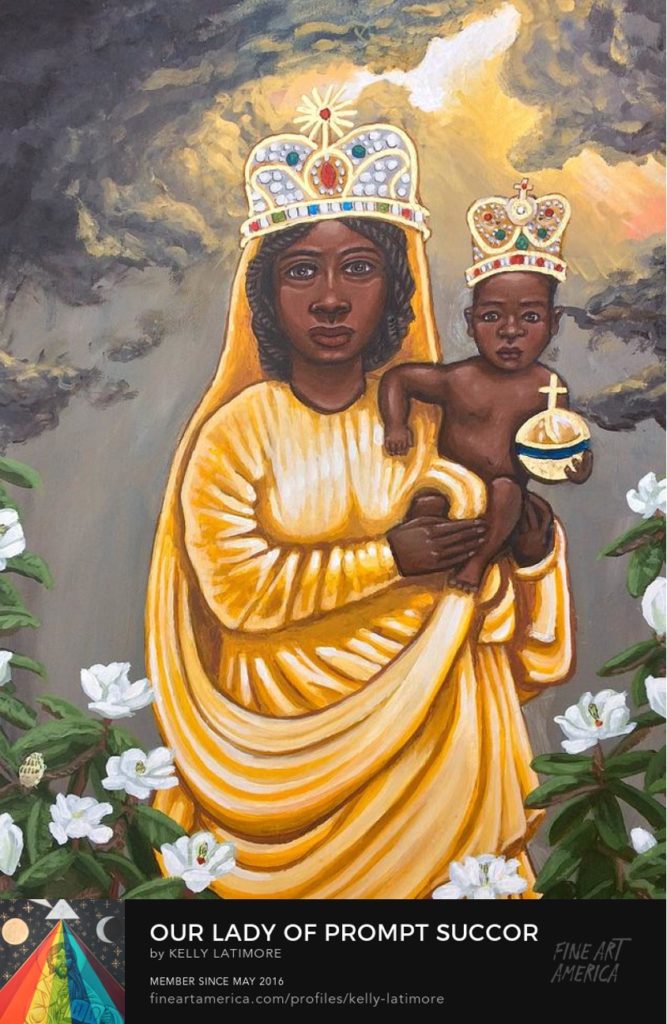
Beginning in January and continuing through March 2023, a series of webinars will present innovative research on cross-cultural approaches to studying the deep past as well as liberation theology and the arts. The first, “Pilgrimage in the Global Middle Ages: Hospitality and Encounter,” will compare medieval pilgrimage practices across the Judeo-Christian, Islamic and Chinese Buddhist traditions to explore commonalities and differences, with particular attention to the themes of hospitality and encounter. The second, “Pilgrimage and the Praxis of Liberation,” will examine theologies of pilgrimage and racial reconciliation. The third, “Sacred Art and the Journey toward Justice,” featuring artist Kelly Latimore, will consider images of the holy encountered at pilgrimage destinations with a focus on Black/Brown iconography in the Christian tradition. Finally, “The Black Madonna for Racial Liberation: A Spirituality to Empower Sacred Activism” will feature Dr. Christena Cleveland, author of God Is a Black Woman, which tells of her pilgrimage to France to see Black Madonna statues. Dr. Cleveland’s public theology models how pilgrimage and story-telling can serve the work for racial equity.

This learning will prepare us to embark on two in-person pilgrimages in April 2023. One will take place in Chicago, where we will visit sites connected to Father Augustus Tolton, the first self-identified African-American man to be ordained a Catholic priest. He is currently one of the six African-American candidates for sainthood. By walking in his footsteps and visiting the site where he died, we will remember Tolton’s witness to the Gospel and his perseverance within the church despite its endemic racism. He strove to realize the church’s mission to be “truly Catholic” and inclusive of all people.

For the second pilgrimage experience, participants will walk through the city of South Bend to landmarks from local African-American and Civil Rights history. We are partnering on this event with the local chapter of Faith in Indiana, a non-profit organization that mobilizes faith leaders to work for racial and economic equity. The goal is to raise consciousness and foster conversation around issues such as access to housing, health care, education, employment, and capital. Along the way, we will hear from speakers immediately impacted by structural violence, make connections between the landmark sites and current issues in local politics, and imagine the kind of community we want to live in – one that is inclusive, equitable and just.
We invite all friends of the MI to join us on the way.
Annie Killian, Ph.D.
Public Humanities Postdoctoral Fellow
Medieval Institute
University of Notre Dame