Chaucer’s Treatise on the Astrolabe has not, historically, won the hearts of many academics—much less the hearts of undergraduates making their first forays into medieval literature. The text is a manual supposedly meant to explain the construction and use of the astronomical tool known as the astrolabe. Most interest in Chaucer’s Astrolabe has focused on its preface, where the author professes to write for his ten-year-old son “Lyte Lowys” (“little Lewis,” l. 1) but also speaks to a much more highly educated audience. In this preface, Chaucer makes claims about medieval education, science, and languages that help us piece together a medieval worldview. Few have ventured beyond these opening lines, however, to understand the mechanics of the astrolabe itself. The task is well worth the effort—Chaucer’s Astrolabe, for all of its technicality, can help us understand the role of science in more traditionally “literary” works like The Canterbury Tales.
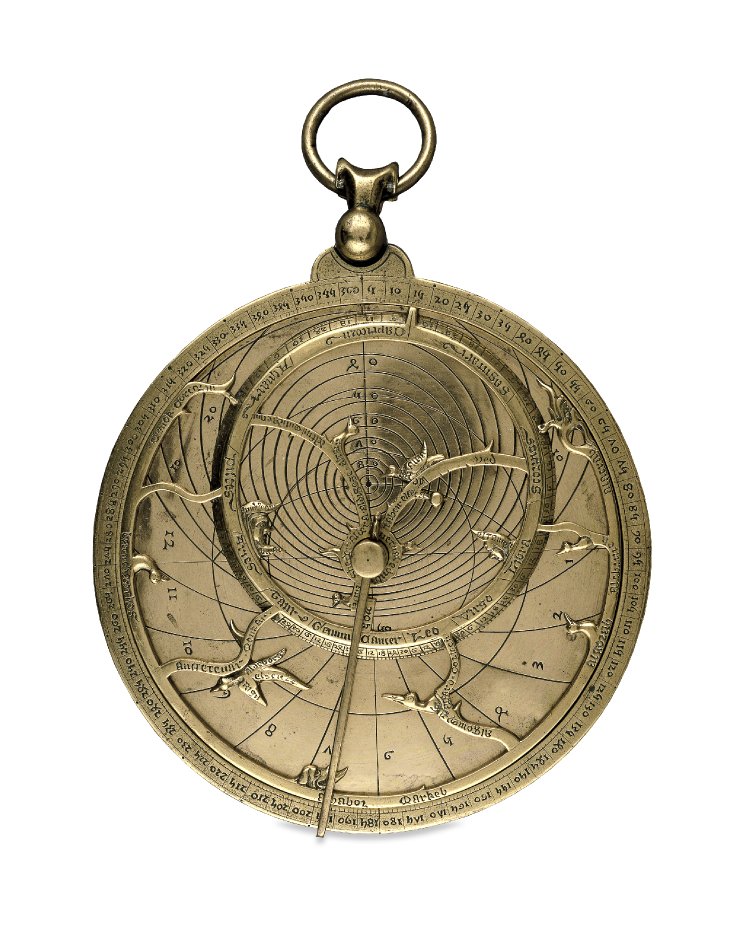

The medieval astrolabe was used by teachers, students, travelers, and astrologers to locate themselves in time and space. The legendary (but likely spurious) story goes that Ptolemy’s camel stepped on his celestial globe and, seeing it flattened on the ground, the Greco-Egyptian polymath was struck with the idea that the celestial sphere could be mapped in two-dimensional terms (Hayton 4). In actuality, the astrolabe developed gradually over the course of centuries—it is a testament to the mixture of ancient Greek, Jewish, and Islamic thought that created the intricate texture of medieval Western science. The astrolabe made particular strides under the Abbasid caliphate in Baghdad, for instance, where it was used to schedule Islam’s five daily prayers. Using geometric principles, it can calculate the time, the date, the position of the sun, and the spread of constellations that the user can expect to see on any given night.
The last of these functions, I like to think, contributed to the intricate sequence of astrological references that threads through The Canterbury Tales. Chaucer frequently matches up a point in time he mentions in his text with the location of the corresponding zodiac sign. The most famous example comes in the initial lines of the Tales’ “General Prologue”: “Whan that Aprill with his shoures soote/ The droghte of March hath perced to the roote” (“At the time that April’s sweet showers have pierced March’s drought to the root,” l. 1-2). Chaucer gives us the approximate date, and follows up soon after with the time of day and the corresponding sign: “and the yonge sonne/ Hath in the Ram his half cours yronne” (“and the young sun has traveled halfway through the Ram [that is, Aries],” l. 7-8). One can imagine Chaucer using his astrolabe to map out the astrological scenes that matched up with the settings of his text.
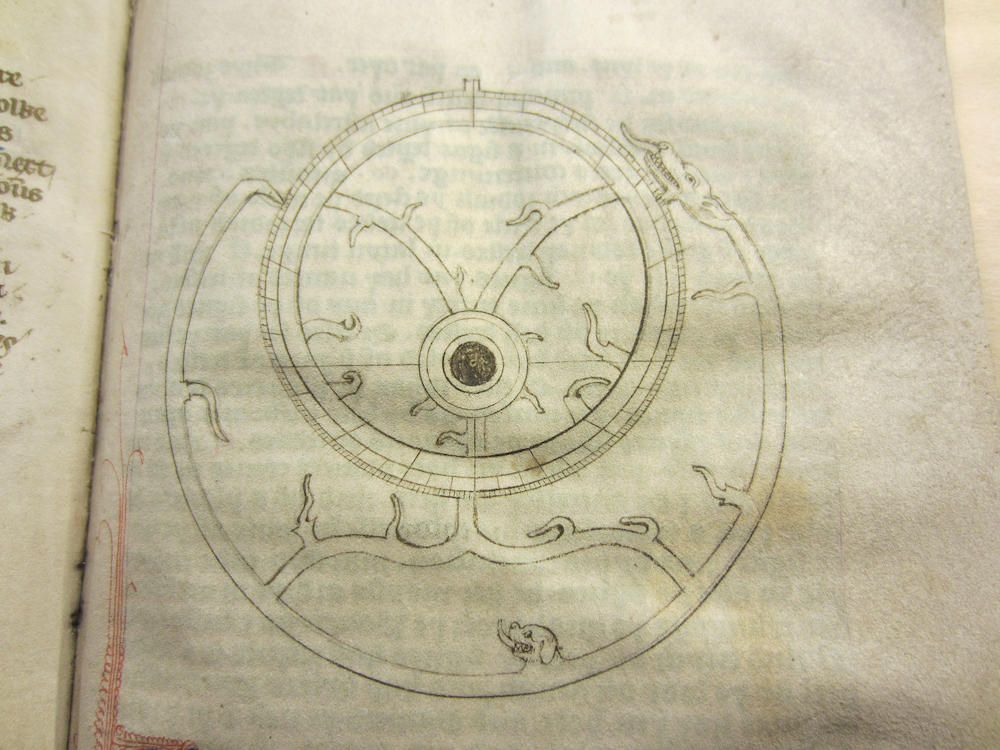
The surviving manuscripts of Chaucer’s Astrolabe show that its early readers experienced it alongside not only scientific texts by astronomers like Abu’Mashar, but also intermingled with poems like the popular French Romance of the Rose—the Astrolabe therefore challenges us to reconsider the divide between the “literary” and the “technical.” In a future post, I will walk step-by-step through my students’ saga to build and use astrolabes this semester. In the meantime, suffice it to say that the experience helps the modern reader to imagine medieval texts within the spatial, visual, and cosmological terms with which their initial audiences would have understood them.
My thanks to Amanda Bohne and Juliette Vuille for their stellar insights and advice.
Erica Machulak
PhD in English
University of Notre Dame
Founder of Hikma Strategies
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Chaucer, Geoffrey. The Riverside Chaucer. Ed. Larry D. Benson. 3rd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2008.
Curry, Walter Clyde. Chaucer and the Mediaeval Sciences. New York: Oxford University Press, 1926.
Hayton, Darin. An Introduction to the Astrolabe. © 2012
Lindberg, David. The Beginnings of Western Science. 2nd ed. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2008.
North, J.D. Chaucer’s Universe. New York: Oxford University Press, 1988.