The information and views set out in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily represent those of the Medieval Institute or the University of Notre Dame.
For Halloween this year, we continue our discussion of rhetorical representations of the monstrous in Beowulf by framing the poem in our current political climate and historical context. In my previous blog, “Mearcstapan: Monsters Across the Border” (July 20, 2018), I explored various interpretations of the Old English compound mearcstapan, used to describe the Grendelkin in Beowulf, and discussed the rhetorical implications of translating the compound as “border-crosser” when teaching or reading the poem in the United States in 2018. Placing the term mearcstapan in conversation with the current administration’s immigration policies (and President Trump’s rhetoric on immigration) emphasizes the othering force of being categorized as immigrant, foreign, or alien. These labels encourage an emotional response due in part to the in-group and out-group dynamics encoded in the language of migration, and the ramifications for certain immigrant groups living in the United States are dire.
/https://public-media.smithsonianmag.com/filer/65/80/6580f645-3d95-4f3b-8e6d-f6a1324bfbb7/06_13_2014_border_crisis.jpg)
In Beowulf, Grendel is repeatedly described as the enemy of the Danish people and is characterized as the arch-nemesis of the heroic protagonist. Beowulf describes the monster as feorhgeniðla “mortal enemy” (969) to the Danish king, Hroðgar, whose hall was the focus of Grendel’s wrath and terror for twelve years. Hroðgar later refers to Grendel as ealdgewinna “old enemy” (1776), a satanic epithet and translation of the Latin hostis antiquus “old enemy.” Although the monster is Hroðgar’s long-time foe, in this description, the Danish king ominously characterized Grendel as something demonic—intuitively or unwittingly reinforcing the narrator’s designation of the Grendelkin as the monstrous progeny of Cain (102-114). This spiritual overlay frames the narrative, and Grendel’s dual characterization as the respective enemy of both the Danes and God is twice corroborated by the narrator’s explicit references to the monster as Godes ondsaca “adversary of God” (786, 1682).
Today, I will consider the Old English satanic epithet feond mancynnes “enemy of the people,” used by the narrator in Beowulf to describe Grendel and modeled on hostis publicus “public enemy” in Latin. The term dates back to Roman antiquity, and the senate famously pronounced emperor Nero a hostis publicus in 68 CE. This epithet has since been leveled against political opponents throughout history and in many languages. The term emphasizes animosity and frames whomever is designated hostis publicus as working against both the will of the people and the greater good. Embedded in this description are pathetical appeals to both fear-mongering and tribalism. Feond mancynnes stresses the majority group (mancynn “mankind” or “the people”) as in a position of moral superiority and opposed to a hostile minority group (feond “the enemy”). This adversarial aspect simultaneously encourages in-group and out-group mentality and emphasizes the danger inherent in hostility.

The epithet ennemi du peuple “enemy of the people” was employed by Maximilien de Robespierre during the French Revolution, and referred to a legally punishable group of socio-political opponents charged with moral depravity and disseminating false news. The epithet vrag naroda [враг народа] “enemy of the people” also gained traction in the Soviet Union because it highlighted economic disparity and social class, emphasizing both the strength of a unified public and the antagonism between the bourgeoisie and proletariat. Once in power, Vladimir Lenin used this epithet to characterize the political leadership of the Constitutional Democratic Party as public enemies in the decree of 1917. Other similar epithets featured prominently in Soviet rhetoric aimed at demonizing socio-political opponents include vrag trudyashchikhsya [враг трудящихся] “enemy of the workers,” vrag proletariata [враг пролетариата] “enemy of the proletariat,” and klassovyi vrag [классовый враг] “class enemy.”

As during the French Revolution, the term became legally formalized in Stalin’s Soviet Union, and similar articles codified versions of the term in other Soviet Republics. Mao Zedong also referred to dissenters as “enemies of the people” in his 1957 speech, On the Correct Handling of Contradictions Among the People. In each appropriation of this epithet, both moral and political animosity is linked to social otherness. The rhetoric of hostis publicus may have been used to depose a tyrant in Roman antiquity, but modern dictators have consistently used the epithet to target their political rivals. More recently, after the Brexit vote in the United Kingdom, the Daily Mail labeled the presiding judges “enemies of the people” for ruling that consent from British Parliament was necessary for departure from the European Union.

The epithet is famously the title of Norwegian playwright Henrik Ibsen’s En folkefiende, “An Enemy of the People” (1882), and Shakespeare appeals repeatedly to this Roman designation in Coriolanus, when Caius Marcius Corliolanus is charged as “chief enemy to the people” (I.I.5), “enemy to the people and his country” (III.III.119) and “[The] people’s enemy” (III.III.138). However, Beowulf and the Old English Juliana also participate in the epithet’s rhetorical tradition and appropriate the Latin political designation by transforming it into a satanic epithet. The Old English feond mancynnes represents an Anglo-Saxon appropriation of the Roman designation, which frames the antagonism in spiritual rather than political terms. In this way, Christian morality is emphasized and opponents are represented as demonic.

This shift reflects the semantic evolution of the Old English feond “enemy” into the modern English “fiend,” which the Oxford English Dictionary defines primarily as “An evil spirit or demon.” In Juliana, the demon who visits the saint is designated a public enemy, thrice referred to as feond moncynnes (317, 523, 630). The demon comes disguised as an angel to deceive the protagonist and tempt her into sin, but Juliana conquers the monster with her saintly virtue. Once she identifies her visitor as demonic, she commands him to disclose his plot: þu scealt furþor gen, feond moncynnes,/ siþfæt secgan, hwa þec sende to me “you must still say further of your journey here, enemy of mankind, and of who sent you to me” (317). The demon boasts how he successfully overcame Nero, Neþde ic nearobregdum þær ic Neron bisweac “I dared venture with wicked tricks when I deceived Nero”(302), but laments that he cannot overpower Juliana:
Næs ænig þara
þæt mec þus bealdlice bennum bilegde,
þream forþrycte, ær þu nu þa
þa miclan meaht mine oferswiðdest,
fæste forfenge, þe me fæder sealde,
feond moncynnes, þa he mec feran het,
þeoden of þystrum, þæt ic þe sceolde
synne swetan.
“There were not any [others] who have so boldly laden me with bonds or overcame me with rebuke, before now when you seized me firmly and overpowered my great strength, which my father gave me, the enemy of mankind, when he commanded me to journey forth, a prince from the darkness, so that I should sweeten your sins for you” (520-525).
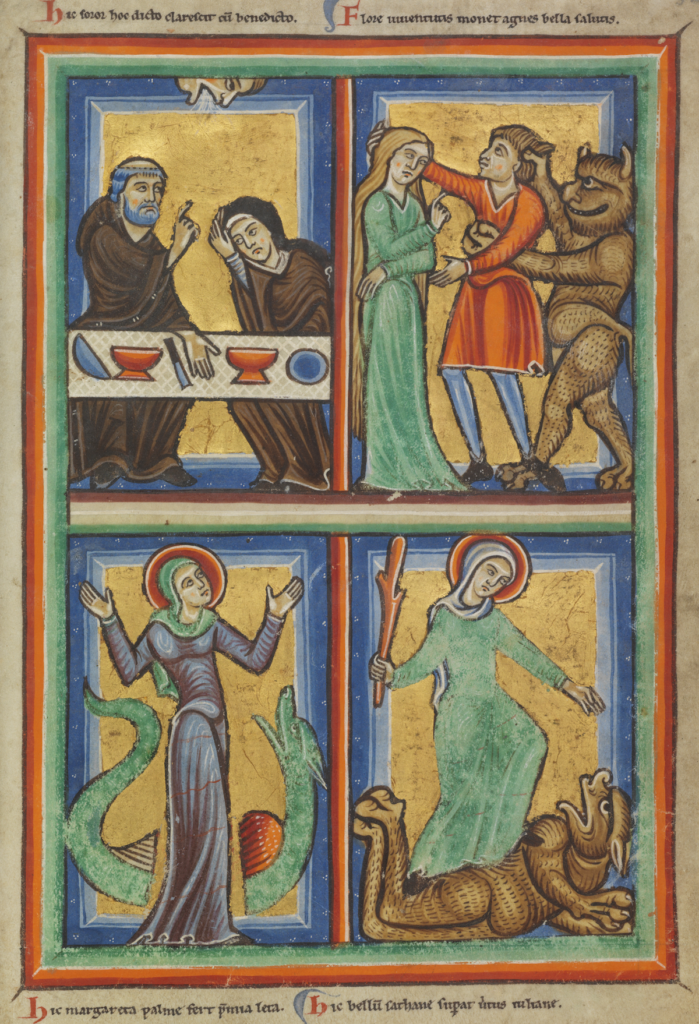

Eventually, seeing that he is no match for Juliana, the demon flees from the saint:
þa seo eadge biseah
ongean gramum, Iuliana,
gehyrde heo hearm galan helle deofol.
Feond moncynnes ongon þa on fleam sceacan,
wita neosan, ond þæt word acwæð:
“Wa me forworhtum! Nu is wen micel
þæt heo mec eft wille earmne gehynan
yflum yrmþum, swa heo mec ær dyde.
“Then blessed Juliana gazed at the angry one, she heard the devil from hell sing his torment. The enemy of mankind began then to retreat in flight, seeking punishments, and spoke these words: “Woe to me, forwrought! There is now a great expectation that she will again humiliate wretched me with evil calamities, as she did to me before” (627-34).
In the first and third instances, the satanic epithet feond moncynnes is used to describe not the demon’s father (i.e. Satan), but rather the demon himself. These references to devils as “enemies of the people” elevate the Roman epithet hostis publicus by presenting the term in a spiritual context, thereby shifting the focus from political opponents to moral adversaries.
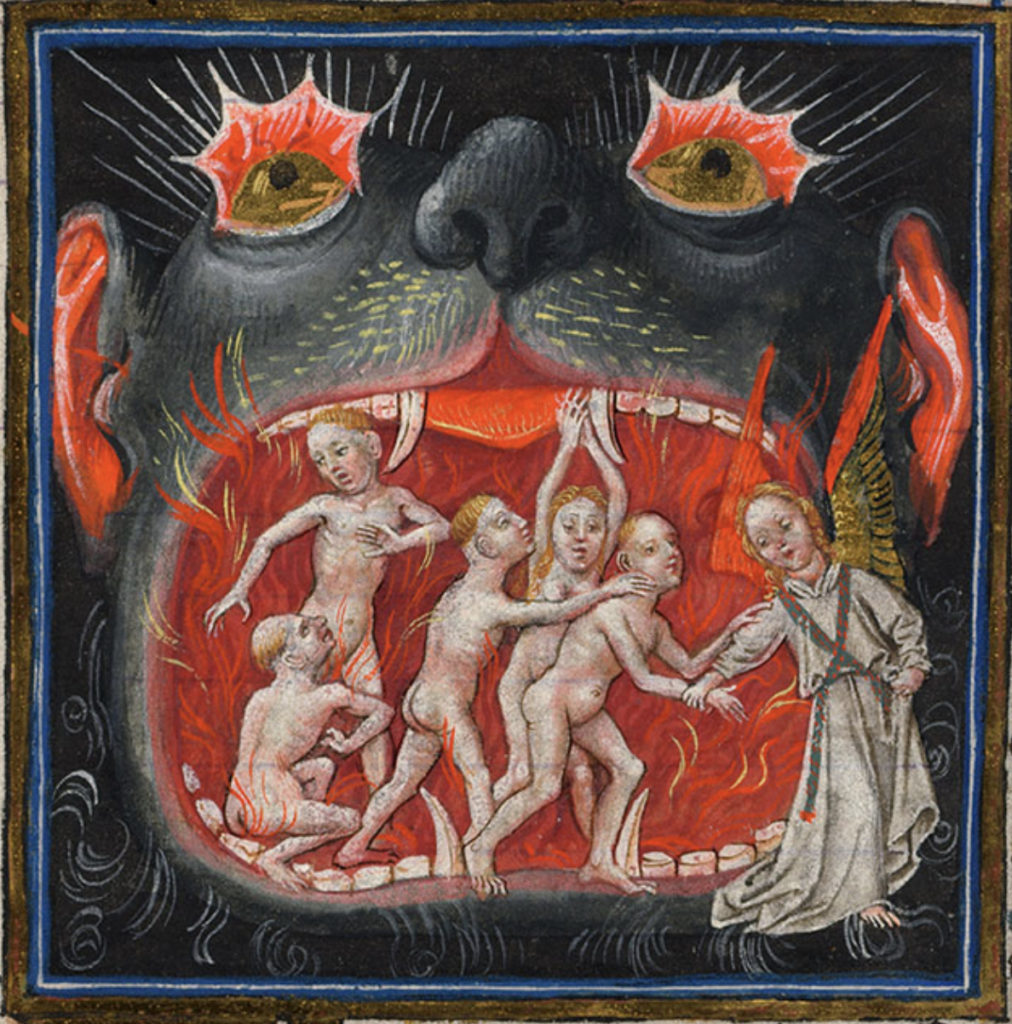

Ælfric refers to the devil as mancynnes feond in two of his Catholic homilies. In one homily, he makes a direct appositive association linking mancynnes feond with awyrigeda deofol “accursed devil” (II.31-32), and in the other Ælfric positions awyrigeda engel “accursed angel” (II.38) in apposition with the satanic epithet. Moreover, mancynnes feond appears in two anonymous Old English homilies. In one of these homilies (contained in Oxford, Bodleian Library, Junius 121), the Latin political epithet hostis publicus is combined with a Latin satanic epithet, hostis antiquus “the old enemy,” and expanded into the Old English epithet se ealda feond mancynnes “the old enemy of mankind.” Additionally, mancynnes feond is used as a satanic epithet in Old English prose hagiographies, twice in a vita of St. Giles and once in two vitae of St. Guthlac.
This demonic epithet also features in Beowulf and is twice used to describe Grendel, marking him as demonic. The narrator characterizes Grendel as feond mancynnes in his initial description of the monster’s carnage wreaked in Denmark:
se æglæca ehtende wæs,
deorc deaþscua, duguþe ond geogoþe,
seomade ond syrede, sinnihte heold
mistige moras; men ne cunnon
hwyder helrunan hwyrftum scriþað.
Swa fela fyrena feond mancynnes,
atol angengea, oft gefremede,
heardra hynða
“The fearsome marauder was attacking the veterans and young warriors, the dark death-shadow lied in waiting and plotted. In the endless night, he ruled the misty marshes. Men did not know whither the hell-wonders glide in turns. So the enemy of mankind, the terrible lone-goer, often performed many crimes, hard humiliations” (159-66).

The narrator’s second reference to Grendel as mancynnes feond comes over a thousand lines later, during his description of Grendel’s defeat:
he þone feond ofercwom,
gehnægde helle gast. Þa he hean gewat,
dreame bedæled, deaþwic seon,
mancynnes feond.
“He (Beowulf) overcame the enemy, humbled the hellish ghost. Then he, the enemy of mankind, departed humiliated to see his death-place, bereft of joy” (1273-76).
In both these descriptions of Grendel, hel “hell” is directly referenced (163, 1274), which both reinforces the satanic undertones implied by feond manncynnes and further signals Grendel’s affiliation with the demonic. By characterizing the monster as “enemy of mankind” (164, 1276), the narrator emphasizes both the existential threat posed by Grendel to the Danish people as well as the spiritual doom which awaits them. The Danes are explicitly condemned as hæðen“heathen” by the narrator (179), especially for offering worship to the devil, described as gastbona “soul-slayer” (177). In this way, physical and spiritual devastation are fused—uniting the political and moral implications of hostis publicus or feond mancynnes represented as a terrifying monster in Beowulf.
Of course, in Trump’s America, the phrase “enemy of the people” calls to mind the president’s repeated use of the term to demonize the media.

President Trump regularly resorts to scare tactics—portending doom—such as when he threatened an economic depression if he were to be impeached. However, the president has especially targeted the media as political and moral adversaries, and their designation as public enemies has resulted in threats of physical violence.
On February 17, 2017, Trump’s rhetorical appropriation of this epithet erupted on Twitter, when the president declared: “The FAKE NEWS media (failing @nytimes, @NBCNews, @ABC, @CBS, @CNN) is not my enemy, it is the enemy of the American People!”
Trump repeated his designation of the press as “the enemy of the people” on February 24, 2018: “A few days ago I called the fake news the enemy of the people and they are. They are the enemy of the people.” On June 25, 2018, the president condemned journalists as “fake newsers” and “the enemy of the people”during a rally. After his summit with Russian President Vladimir Putin in Helsinki, Finland (July 15, 2018), in his response to criticism by the press, Trump tweeted on July 19, 2018: “The Summit with Russia was a great success, except with the real enemy of the people, the Fake News Media.”

Trump has drawn criticism from international organizations such as the United Nations and the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights for his targeting of journalists and the institution of the free press. Still, the president’s attacks on the media have continued, despite that his administration is investigating the abduction and apparent murder of Jamal Khashoggi, a journalist for The Washington Post. Turkish media reports that he was tortured, executed and dismembered shortly after entering the Saudi consulate in Istanbul on October 2, 2018. Despite political pressure, the president has not toned down his rhetoric, and Trump praised Montana Republican Rep. Greg Gianforte for assaulting a reporter on October 19, 2018. The president applauded Gianforte’s violence and complimented the GOP Congressman saying, “any guy who can do a body slam, he’s my kind of… he’s my guy.”

While rhetorical demonization of political opponents as “enemies of the people” is by no means new, in the past it has proven effective in arousing fear and hatred, paving the way in many cases for atrocities. By painting the free press as a public enemy, Trump has appropriated this political designation (and satanic epithet), applying it to those who would criticize him and sanctioning violence against them. The president uses the term as a rhetorical weapon—a tool which both challenges the credibility of his dissenters and conjures the specter of conspiracy against him. Even this past week, after pipe-bombs were sent to some of his most prominent political targets (including CNN and members of the previous administration), Trump persisted in his rhetoric against the media. Despite the ongoing manhunt for a serial bomber (which apprehended the alleged perpetrator, Cesar Soyac), the president tweeted on October 25, 2018: “A very big part of the Anger we see today in our society is caused by the purposely false and inaccurate reporting of the Mainstream Media that I refer to as Fake News. It has gotten so bad and hateful that it is beyond description. Mainstream Media must clean up its act, FAST!”
Trump followed this up a few days later with another tweet, again designating the media as enemies of the people and blaming the free press for the recent surge in politically motivated violence, declaring on October 29, 2018: “There is great anger in our Country caused in part by inaccurate, and even fraudulent, reporting of the news. The Fake News Media, the true Enemy of the People, must stop the open & obvious hostility & report the news accurately & fairly. That will do much to put out the flame…”
Until Trump’s presidency, attacks against the free press were primarily associated with the Nazi regime, which appropriated the 19th century political term lügenpresse “lying press” for their propaganda efforts against the free press in Germany. However, the alt-right movement in the United States has more recently appropriated this Nazi epithet to attack the media as pathological liars, and the president has adopted this rhetorical position. The New York Times has pointed out that the president’s demonization of the media frequently follows moments of crisis and criticism, comparable to the propagandizing use of lügenpresse by Nazis and vrag naroda by Soviets.

When Trump designates the free press as “the enemy of the people,” he appeals to the political tradition of hostis publicus, but invokes also a moral—even spiritual—component emphasized in the satanic epithet feond mancynnes used for the demon in Juliana and Grendel in Beowulf. The president has weaponized the rhetoric of monstrosity against his most vocal critics and whistleblowers, those who might hold him accountable for his actions through their reporting or political opposition. In placing Old English literature (such as Beowulf and Juliana) in conversation with global trends in political rhetoric, we find that the epithet feond mancynnes resonates with Trump’s ethical appeals and demonization of the media as “the enemy of the people.” In this way, the rhetoric of monstrosity displayed in these medieval poems can speak to the current crisis of credibility plaguing American politics. The narrator’s designation of Grendel as feond mancynnes sanctions vengeance against him in Beowulf, and similarly the president’s rhetoric both condones and encourages violence against the free press and his political adversaries.
Richard Fahey
PhD Candidate in English
University of Notre Dame
Further Reading
Feldman, Thalia Phillies. “A Comparative Study of Feond, Deofl, Syn, and Hel in Beowulf.” Neuphilologische Mitteilungen 88 (1987): 159-74.
—. “Grendel and Cain’s Descendents.” Literary Onomastics Studies 8 (1981): 71-87.
Orchard, Andy. Pride and Prodigies: Studies in the Monsters of the ‘Beowulf’-Manuscript. Cambridge: D. S. Brewer, 1995.
—. A Critical Companion to A Critical Companion to ‘Beowulf’. Cambridge: D. S. Brewer, 2003.
Vinsonhaler, Chris. “The HearmscaÞa and the Handshake: Desire and Disruption in the Grendel Episode.” Comitatus 47 (2016): 1-36.