Although it does not often get the same attention as other wondrous and fiery creatures, such as dragons, the marvelous phoenix has an equally deep and ancient history. One of the oldest known accounts of the phoenix myth comes from Horapollo’s Hieroglyphica, translated into ancient Greek around the 5th century B.C.E. The phoenix, called benu by the Egyptian author, becomes increasingly popular, appearing in works by Greek authors, such as Herodotus’s Histories and Antiphanes of Athens’ Homopatrioi, and in works by Latin authors, such as Tacitus’s Annals, Ovid’s Metamorphoses, Pliny the Elder’s Natural History, and of course Lactantius’ De ave phoenice, which is adapted, expanded and allegorized in the Old English Phoenix poem found in the medieval codex known as the Exeter Book (Exeter Cathedral Library MS 3501).
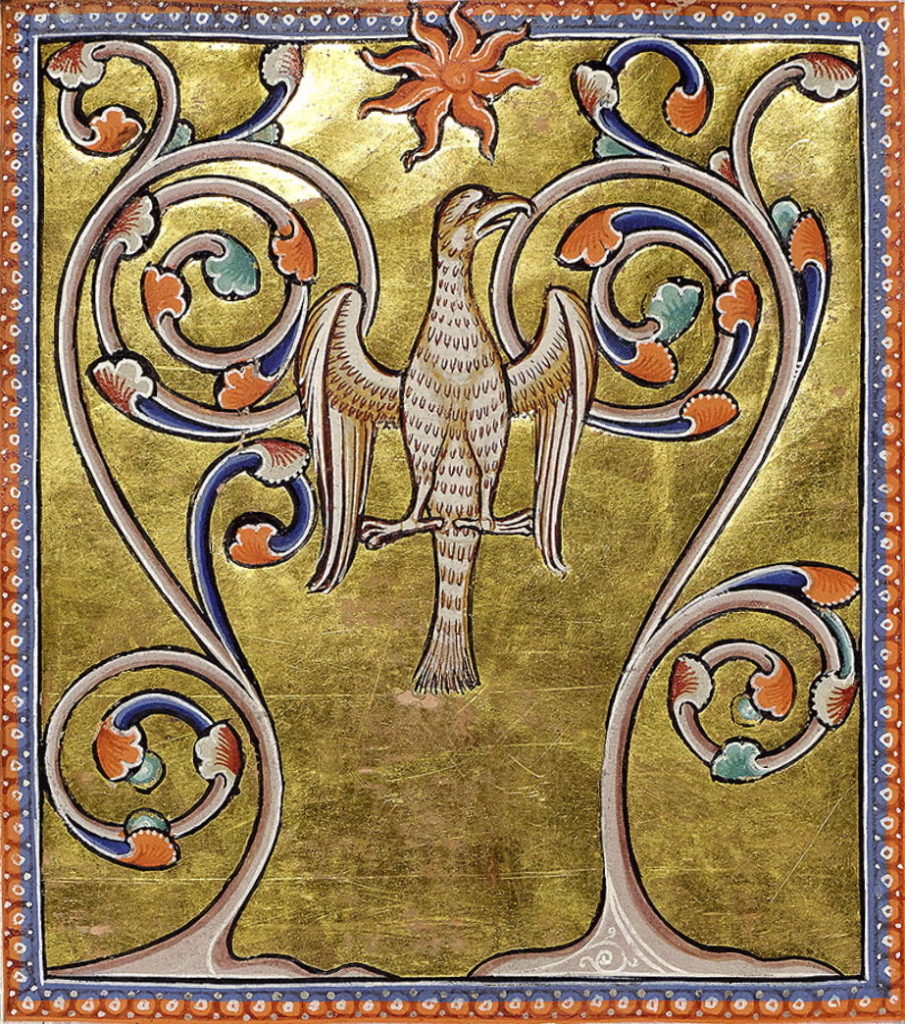

As I mentioned in my previous blog centered on translating the Exeter Book Phoenix, the phoenix bird also appears in the Abrahamic tradition, from the bird of paradise (chol) in commentaries on Jewish scripture (especially the Midrash and Talmud) to the phoenix’s allegorization and comparisons with Christ himself by early Christian authors. Sometimes, these early Christian authors would use the phoenix as evidence for the possibility of Christ’s resurrection, as can be observed in Clement of Rome’s Epistula ad Corinthos, Tertullian’s De resurrectione carnis, St. Epiphanius’ Physiologus and in St. Ambrose’s De excessu Satyri. This moralizing interpretation of the phoenix extends into the modern era and continues unto our own contemporary age.
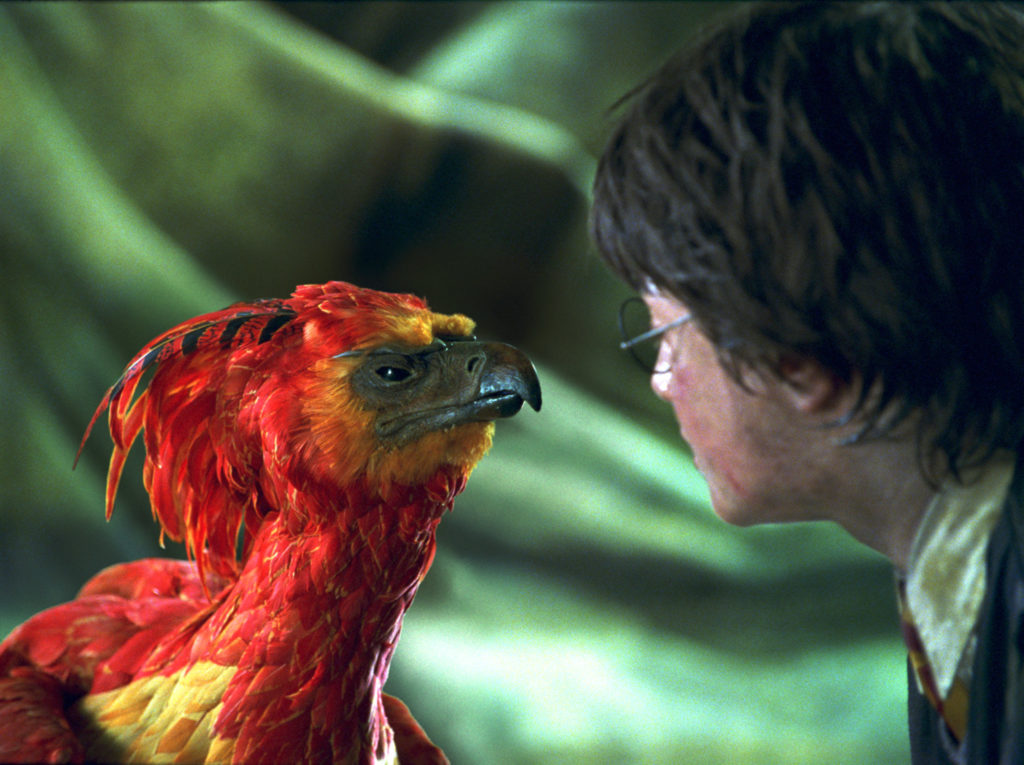

Within the realm of fantasy literature and popular fiction, Harry Potter & the Order of the Phoenix highlight the longstanding association with the phoenix and moral goodness, in this book the day-saving gang of noble, good and trustworthy witches and wizards, also called as Dumbledore’s army, are known as the Order of the Phoenix. It is this group which twice stands up to Voldemort and his Death-eaters, and each time they succeed.
Indeed, the ultimate white wizard in J.K. Rowling’s fantasy world, Albus Dumbledore, has his own pet phoenix named Fawks, who swiftly delivers the sword of Godrick Gryffindor to Harry Potter in his moment of need and bravely pecks the monstrous basilisk’s eyes out in The Chamber of Secrets. Later, Fawks saves his master from unpleasant arrest and an uncomfortable stay in the magical prison Azkaban in The Order of the Phoenix. This extremely positive association is likely a result of medieval Christological allegory often linked the phoenix, which parallels Christ in its death and rebirth.
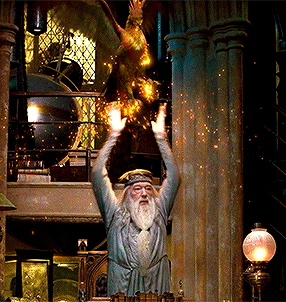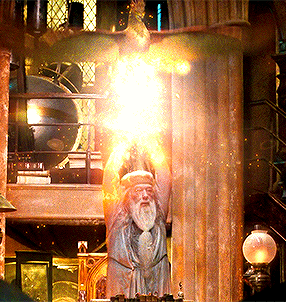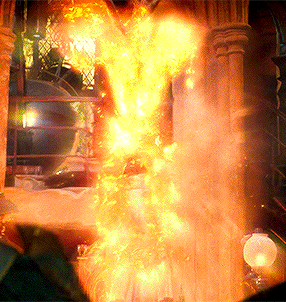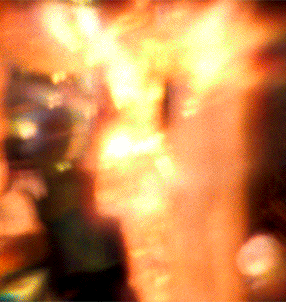
In the Exeter Book Phoenix, this allegory is emphasized and dramatized as the phoenix is aligned with both paradise in heaven and compared to the westward journey of the sun. Moreover, the mythical bird—like the sun—is repeatedly connected to images of glistening treasure and beautiful jewels. In my translation of the Old English Phoenix, lines 85-119, I do my best to preserve as much of the original poem’s language and semantics as possible, and even at times imitate the cadence, but as with my earlier translation of previous lines 1-49, I take certain creative liberties and mobilize poetic licensure when I feel it enhances my English translation.
Stay tuned for additional forthcoming translations from the Exeter Book Phoenix, reborn as modern English poems!
Richard Fahey
PhD in English
University of Notre Dame
Further Reading
Badke, David. “Phoenix.” The Medieval Bestiary, 2022.
Fahey, Richard. “The Phoenix (85-119).” Medieval Studies Research Blog: Medieval Poetry Project, 2022.
—. “Resurrecting the Phoenix.” Medieval Studies Research Blog, 2015.
—. “The Phoenix (1-49).” Medieval Studies Research Blog: Medieval Poetry Project, 2015.
Fahs, Maria. “Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them in Medieval Bestiaries.” Medieval Studies Research Blog, 2015.
Hill, John Spencer. “The Phoenix.” Religion and Literature 16.2 (1994): 61-66.
Kosloski, Philip. “Christian symbolism of the Phoenix (and why we chose it for our new comic book).” Voyage, 2021.
—. “This is how the phoenix became a Christian symbol.” Aleteia, 2017.
Niehoff, M. R. “The Phoenix in Rabbinic Literature” The Harvard Theological Review 89.3 (1996).]: 245-265.
Petersen, Helle Falcher. “The Phoenix: The Art of Literary Recycling” NM 101 (2000): 375–386.
Steen, Janie. Verse and Virtuosity: the adaptation of Latin rhetoric in Old English poetry. University of Toronto Press: Toronto, ON, 2008.
Sorensen, Ingrid. “Dumbledore’s Phoenix and the Medieval Bestiary.” Getty: Book of Beasts, 2018.
Videen, Hana. “Phoenix.” Dēor-hord: a Medieval and Modern Bestiary, 2016.
