by Aedín Ní Bhróithe Clements, Irish Studies Librarian
This immigrant librarian was delighted to see Ireland’s national holiday celebrated in American elementary schools. It was dismaying, however, to walk down a school corridor in March of 1996, and see the walls bedecked with rainbows, crocks of gold, and leprechauns.
Did a film about a leprechaun and a crock of gold so captivate American audiences that no other stories could compete? Have books of Irish stories been available for children who grew up in America in the last century?

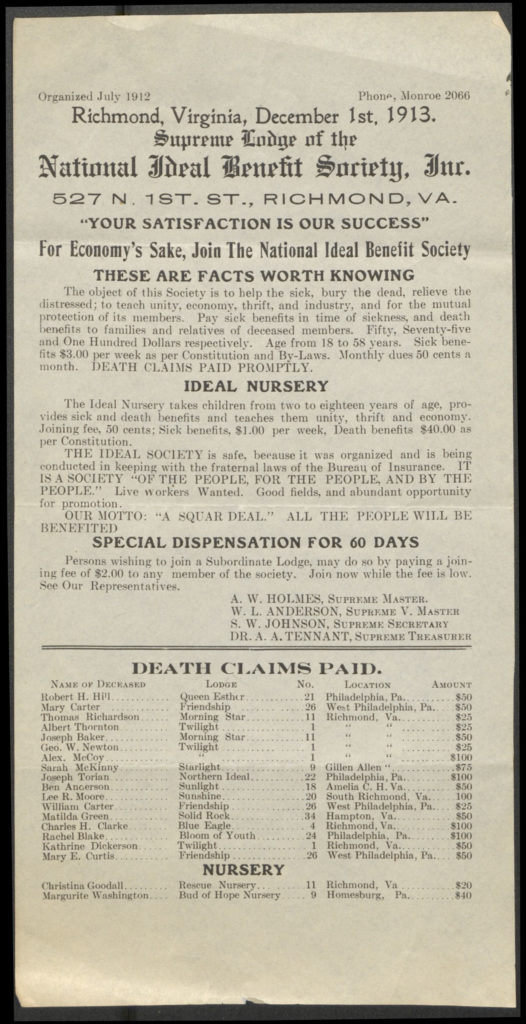
Rare Books Medium PR 6005 .O38 K54 1921
Padraic Colum (1881-1972) and Ella Young (1867-1956) are the only Irish authors whose books have been recognized with a Newbery honor. The Newbery medal was founded in 1922 and is awarded annually by the ALA for an American-published children’s book. In addition to the medalist, a few books are named honor books each year. Colum and Young are also among the few Irish authors mentioned in American reviews of children’s books in the first half of the twentieth century.
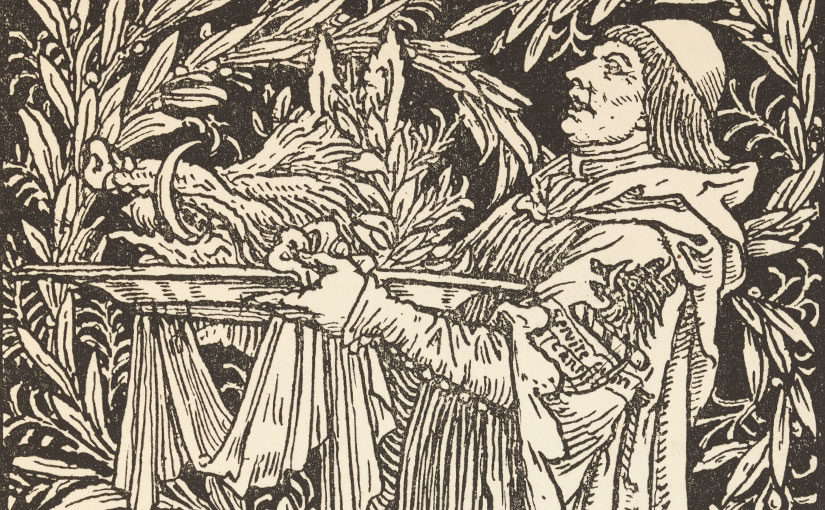
Colum’s The King of Ireland’s Son, illustrated by Willy Pogány, has many stories woven into a framing narrative. Between the time when Connal, the King of Ireland’s son, is sent on a quest by the Enchanter and the end where he and Fedelma, the Enchanter’s daughter are finally married, there are many stories and adventures, some concerning Connal and Fedelma, and some being stories told by our characters — stories within stories.
As in all Colum’s books for children, the art of the storyteller is always close to the surface.

And then a flock of ravens came from the rocks, and flying straight at them attacked Fedelma and the King of Ireland’s Son. The King’s Son sprang from the steed and taking his sword in his hand he fought the ravens until he drove them away. They rode on again. But now the ravens flew back and attacked them again and the King of Ireland’s Son fought them until his hands were wearied. He mounted the steed again, and they rode swiftly on. and the ravens came the third time and attacked them more fiercely than before. The King’s Son fought them until he had killed all but three and until he was covered with their blood and feathers.
Colum, 51

Rare Books Medium PR 6005 .O38 G57 1919
Colum’s children’s books, published by Macmillan, are drawn from the literature of a number of countries and cultures. His The Golden Fleece and The Children’s Homer were much-read and constantly recommended for youth, and his Hawaiian stories were written at the request of the Hawaiian legislature. His Irish stories include The Girl who Sat by the Ashes, and The White Sparrow, and The Forge in the Forest is a collection of stories of different cultures all told in a forge, a traditional setting for storytelling.
Typically, Colum’s books have stories within a story, so that the narrator and context of the storytelling is part of the story. In The Big Tree of Bunlahy, for example, the narrator sets the scene by claiming that the big elm tree in his small native village is world-famous. The narrator proceeds to tell of many instances where he sat under the tree as a boy, often in the context of an errand such as a visit to the shoemaker, and he tells of a colorful series of people who gathered under the tree, and the stories that they told on different occasions. Stories vary from early Irish literature such as the story of Oisín (Usheen) and Tír na nÓg, to stories about animals and birds.
Colum’s children’s books are just one aspect of the literature for which he was known. He was already well-known in Ireland as a playwright and a poet when he left for America in 1914. In fact, he is mentioned in Joyce’s Ulysses as one of Ireland’s most promising young writers in 1904.
In his long career in America he taught literature at Columbia University in New York, sometimes co-teaching along with Mary Colum, his wife.

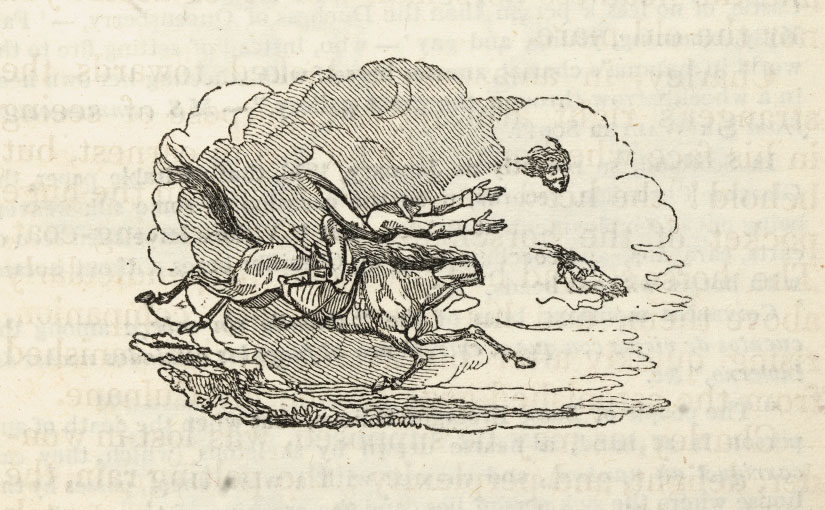
Another Irish emigrant, Ella Young, who made her home in California in the 1920s, was involved, as Colum was, in the Irish Literary Revival. She, too, taught in a university. She taught Irish myth and lore at the University of Berkeley in California. And Irish myth and lore is at the center of her books of stories for children. Shown above is her 1932 book, The Unicorn with Silver Shoes, illustrated by Robert Lawson.

Rare Books Medium PS 3547 .O4745 W66 1927
The Wonder Smith and His Son was a Newbery Honor book in 1928, and The Tangle-Coated Horse and Other Tales was a Newbery Honor book in 1930.
The Wonder Smith is Young’s name for An Gobán Saor, a mythical builder, stonemason and trickster, who figures in many Irish folktales. The title page by Boris Artzybasheff, with its decorations inspired by the designs on Irish illuminated manuscripts, enhances the idea of these tales orginating in ‘the golden childhood of the world’.

It is interesting that the works of these two writers of the Irish Revival, settled in America, were selected by American publishers and reviewers alike. They represent a new image of Ireland for American readers, one of a nation with its own folklore and literary traditions. Earlier books such as Only an Irish Boy by Horatio Alger, told stories of Irish immigrant children who ‘made good’ in America, and so the insistence of these writers on the existence and richness of Ireland’s culture was probably very welcome.
Our Fall 2013 exhibit was on Irish children’s literature, and we hope to have a selection from that exhibit online in the near future.
Happy St Patrick’s Day to you and yours
from all of us in Notre Dame’s Special Collections!
St Patrick’s Day 2018 post: St. Patrick’s Day in America (1872)
St Patrick’s Day 2019 post: St. Patrick and the Nun of Kenmare
St Patrick’s Day 2020 post: St. Patrick’s Day Postcards
Or, you can browse all our Irish Studies related posts.