by Rachel Bohlmann, American History Librarian and Curator
Rare Books and Special Collection recently acquired a Civil War broadside (a.k.a., poster) that was published very early in the conflict, probably in August or September 1861. Produced and printed in Boston, the map provided a Northern perspective on the war as it had unfolded to that point and offered reassurance about the conflict’s ultimate outcome. First, the broadside’s creators remind viewers that despite the Confederacy’s initial victories—at Fort Sumter in April and the Battle of Bull Run in July—the Union had prevailed in a battle for continued control of Fort Monroe, near Norfolk, Virginia, in May. The stronghold was strategically significant for Union designs on the Confederate’s capital at Richmond. Secondly, the broadside’s authors convey confidence that the North’s superior population and larger economy would ultimately prevail.
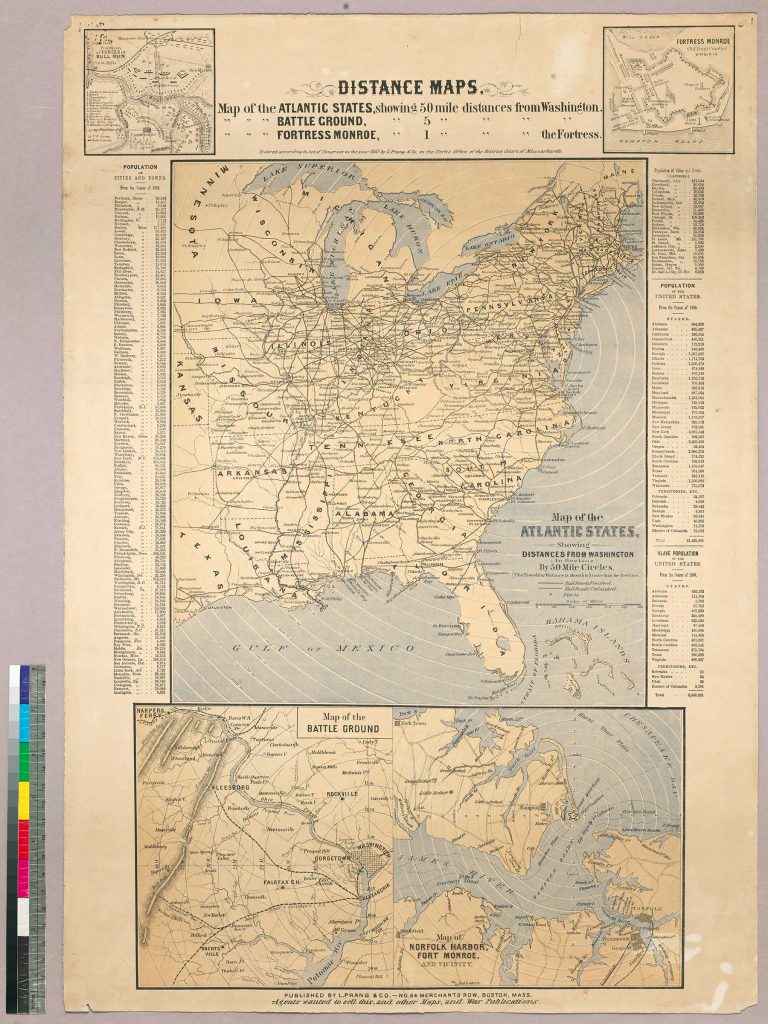
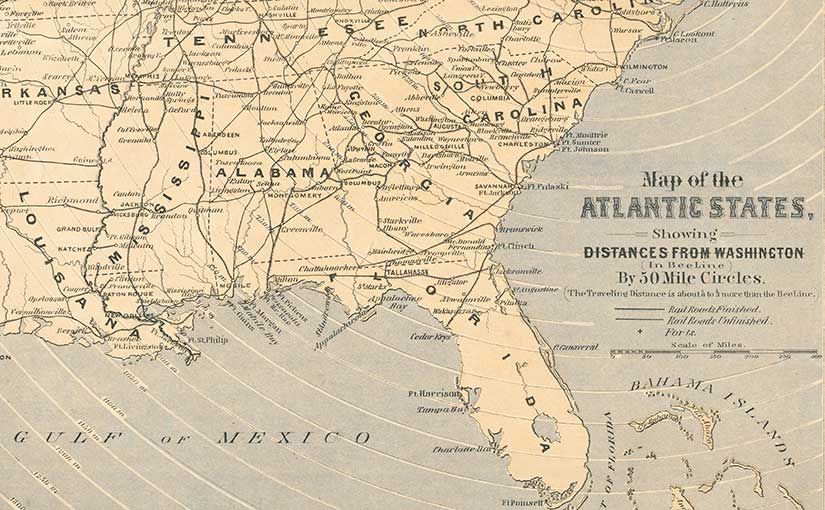
The broadside’s most prominent feature is its three distance maps. The largest is a railroad map of the United States that shows distances from Washington, D.C. One of two smaller maps indicates distance from Washington to an unnamed battle ground, which people at the time would have understood as the Battle of Bull Run, just 30 miles from the capital. The Confederates had recently routed Union forces there, an outcome that worried many Northerners who had, until that point, expected a quick and decisive end to the war.
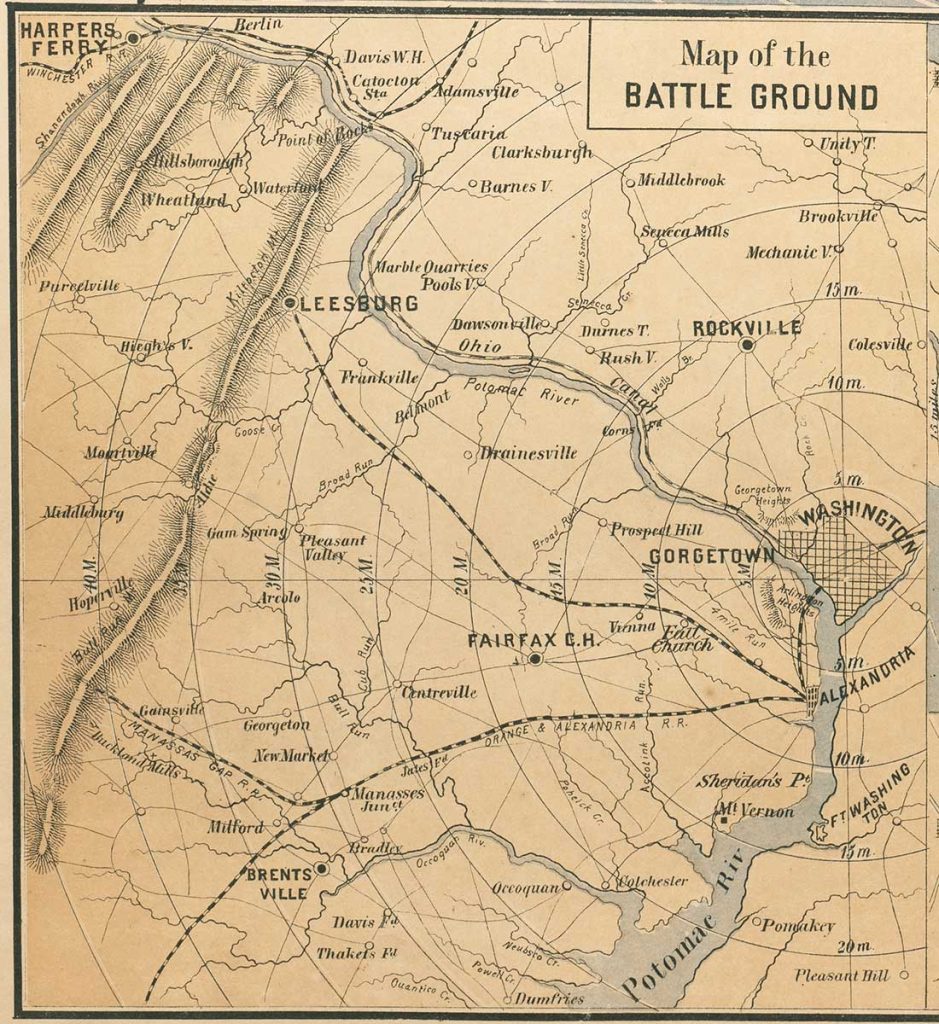
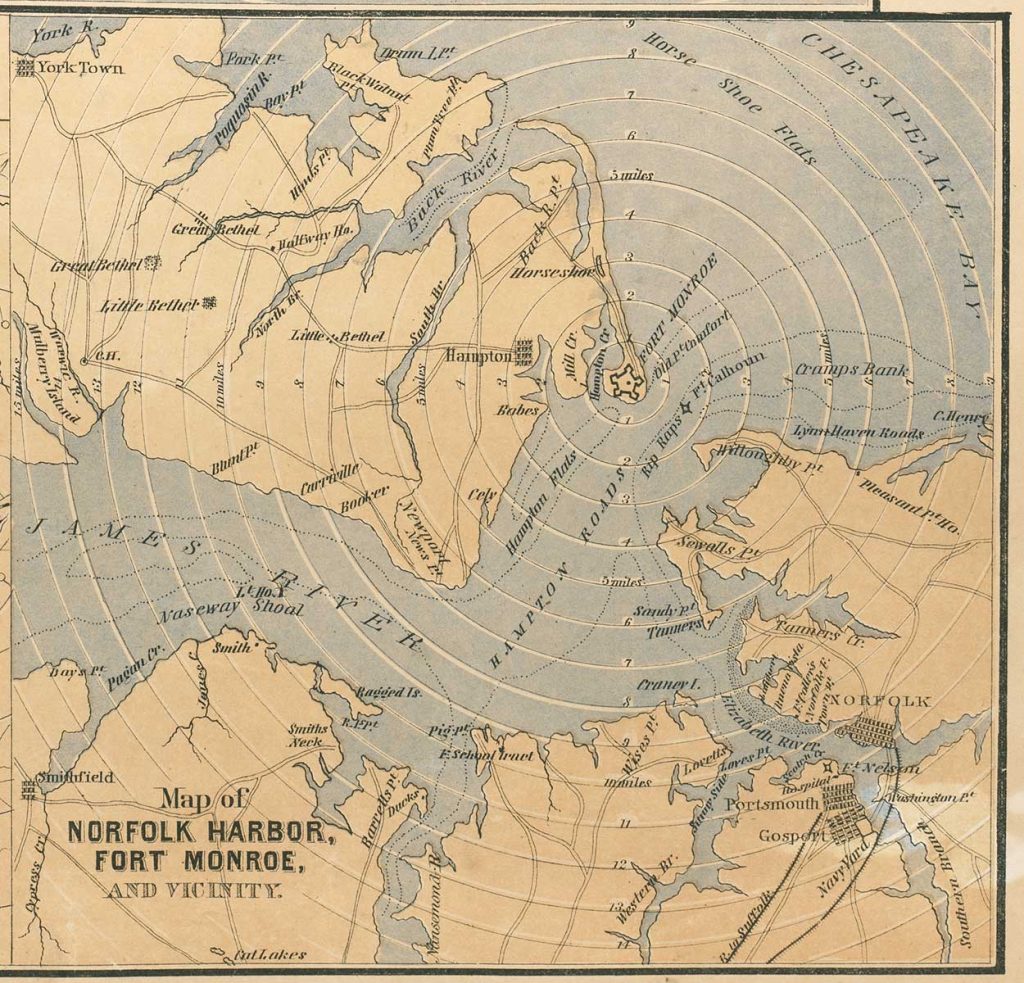
The third distance map shows a detail of Norfolk Harbor and Fort Monroe, the site of a recent Union victory. The fortress remained in Union control throughout the war.
Finally, this broadside provides population figures for the nation’s cities and towns, and states, as well as the number of enslaved people in states and territories. This data reinforced what even a glance at the railroad map implied: the North’s more developed industrial and economic infrastructure along with its superior numbers pointed to an eventual Union victory.
A happy Memorial Day to you and yours
from all of us in Notre Dame’s Special Collections!
2023 post: A Woman’s Reporting on the Bonus Army in Depression-Era Washington
2022 post: Representing Decoration Day in a 19th Century Political Magazine
2021 post: An Early Civil War Caricature of Jefferson Davis
2020 post: Narratives about the Corby Statues—at Gettysburg and on Campus
2019 post: Myths and Memorials
2018 post: “Decoration Day” poem by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow
2017 post: “Memorial Day” poem by Joyce Kilmer
2016 post: Memorial Day: Stories of War by a Civil War Veteran
Rare Books and Special Collections is closed today (May 27th) for Memorial Day and will be closed on July 4th for Independence Day. Otherwise, RBSC will be open regular hours this summer — 9:30am to 4:30pm, Monday through Friday.
Please note that the 14th floor of the Hesburgh Library is under renovation from May 20 to August 9. The Library Circle, East, and South Entrances will be blocked off intermittently during this time. See the logistics map for additional details.