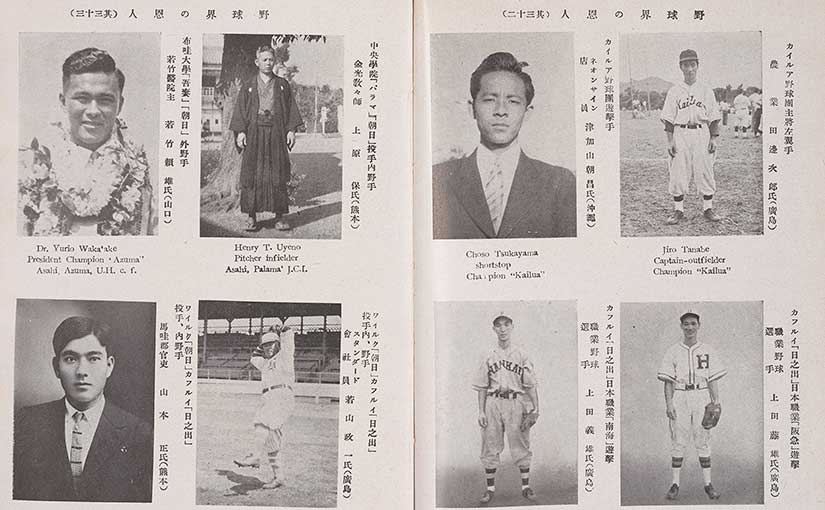
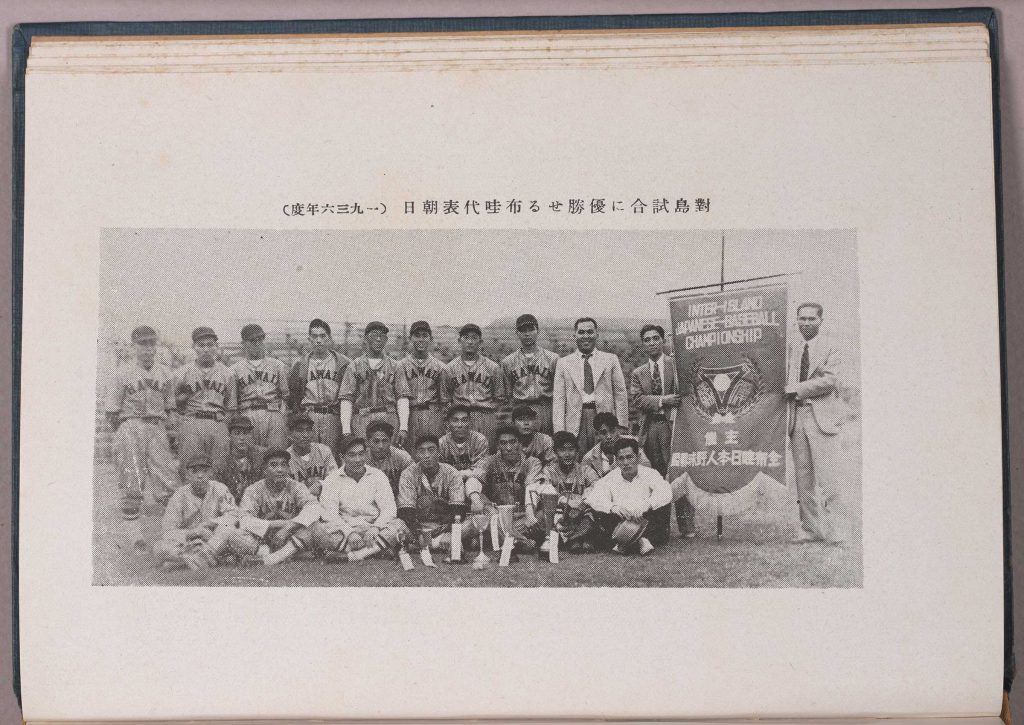
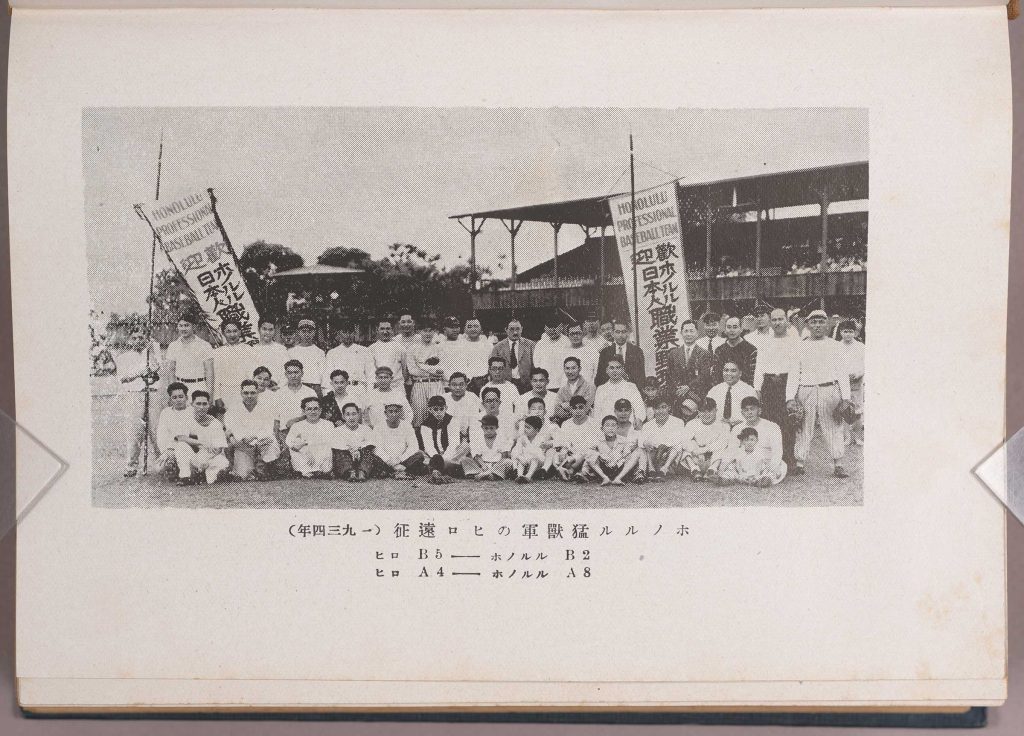
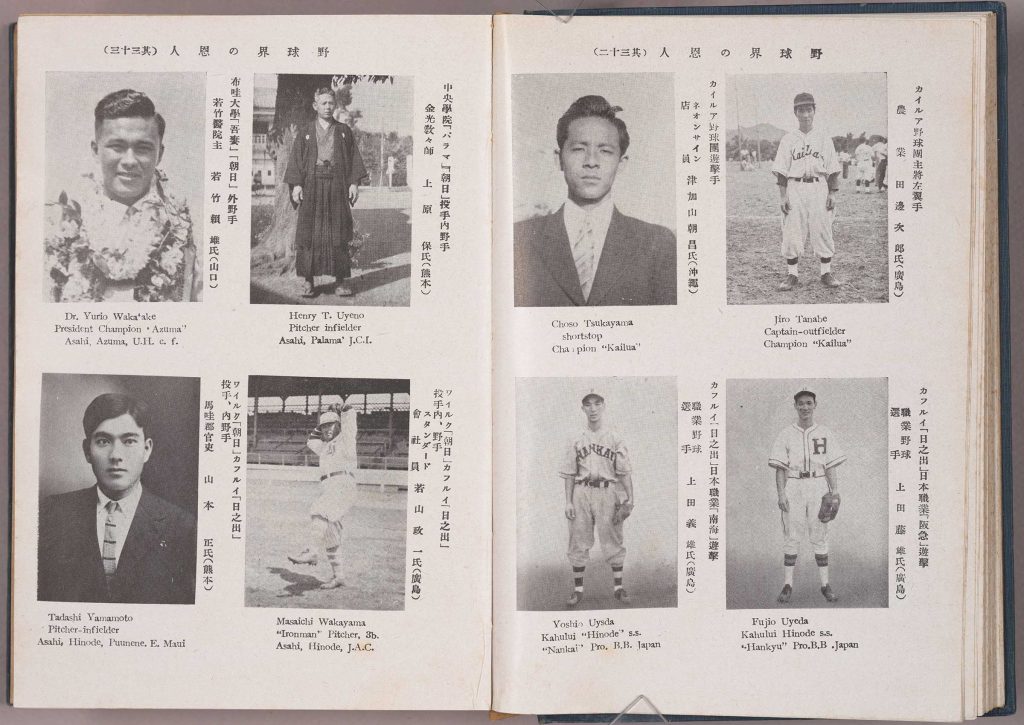
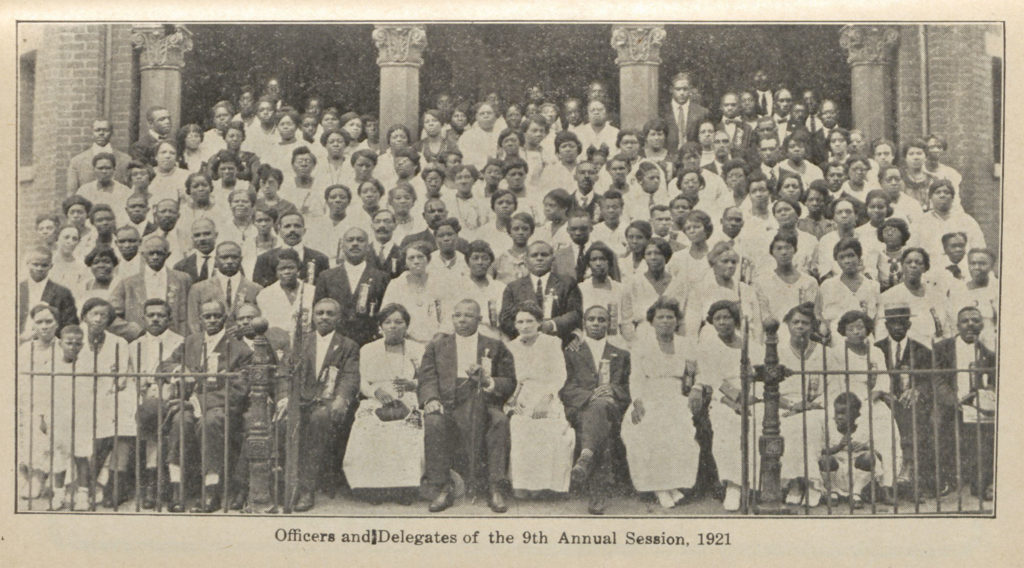
We join with The Library of Congress, National Archives and Records Administration, National Endowment for the Humanities, National Gallery of Art, National Park Service, Smithsonian Institution and United States Holocaust Memorial Museum in paying tribute to the generations of African Americans who struggled with adversity to achieve full citizenship in American society.
“Play Ball With Jackie”: Unboxing the Jackie Robinson Doll for Black History Month
by Greg Bond, Sports Archivist and Curator, Joyce Sports Research Collection
In recognition of Black History Month, Rare Books and Special Collections is pleased to highlight its recent acquisition of the Jackie Robinson Doll, a 13-inch plastic composition doll of the baseball icon manufactured by the Allied-Grand Doll Manufacturing Company of Brooklyn, N.Y. in 1950.

The moveable and posable doll was sold fully accessorized with Robinson’s complete Brooklyn Dodgers uniform, miniature baseball equipment, and other accompanying commemorative items. The Jackie Robinson Doll was one of the earliest realistic African American dolls aimed at the general mainstream toy market and was a testament to the popularity and importance of Robinson, who several years earlier had famously broken major league baseball’s long-standing color line against Black players.


Despite Robinson’s widespread celebrity, the Jackie Robinson Doll was unusual on toystore shelves in 1950. Although African American designers and companies had long made dolls specifically targeted at the Black community, most mainstream American toy manufacturers at the time did not create realistic dolls depicting African Americans. As historian Rob Goldberg explains in his book Radical Play: Revolutionizing Children’s Toys in 1960s and 1970s America for most of the early twentieth century there had “been a painful history of demeaning representations and unjust exclusions of African Americans by the nearly all-white producers of mass-market toys” (page 86).
The story of the Jackie Robinson Doll began after the 1949 season when Robinson had won the National League’s Most Valuable Player Award. Over that winter, Robinson sought opportunities for extra income—especially during the off season—to support his growing family. He partnered with entertainment lawyer Martin Stone in hopes of capitalizing on his success and popularity to supplement his baseball salary. As later explained in a 1951 New York Herald Tribune article: “One day in 1949, Jackie Robinson walked into his [Martin Stone’s] penthouse office and wondered how he could make some money during the winter—up to then he’d been selling television sets in the off-season.”
Within the next couple of years, Robinson and Stone built a successful marketing campaign that produced the Hollywood motion picture The Jackie Robinson Story, a series of six Jackie Robinson comic books (featured in a previous RBSC blog post), the Jackie Robinson Radio Show broadcast on New York’s WNBC, t-shirts, and, in total, “about thirty franchises,” according to the Herald Tribune.


The Jackie Robinson Doll, which was sold individually or as a packaged set with the first issue of the recently published Jackie Robinson comic book, was another popular branded item that received considerable public attention. The doll was one of only a handful of items mentioned by name in a March 1950 newspaper article, “Toy Fair Opened; 100,000 Items for the Yule Trade on View.”


Toy dealers widely advertised the doll in newspapers around the country. An ad in the Alabama Tribune, an African American newspaper in Montgomery, Alabama, informed potential customers: “Here he is! Jackie Robinson in doll form dressed in his Dodger’s uniform. Doll comes boxed with ball bat, sweatshirt, baseball game, and the life story of the great hero!” Similarly, the Harrisburg (Pa.) Patriot-News daily newspaper ran an ad for the local Bill’s department store that described Robinson as “America’s Favorite Athlete.” The store declared, “First time in Harrisburg … everybody can have a doll of America’s Athletic hero.” In May 1950, the Associated Negro Press reported that the Jackie Robinson doll was even in stock at the famous Macy’s department store in New York City.

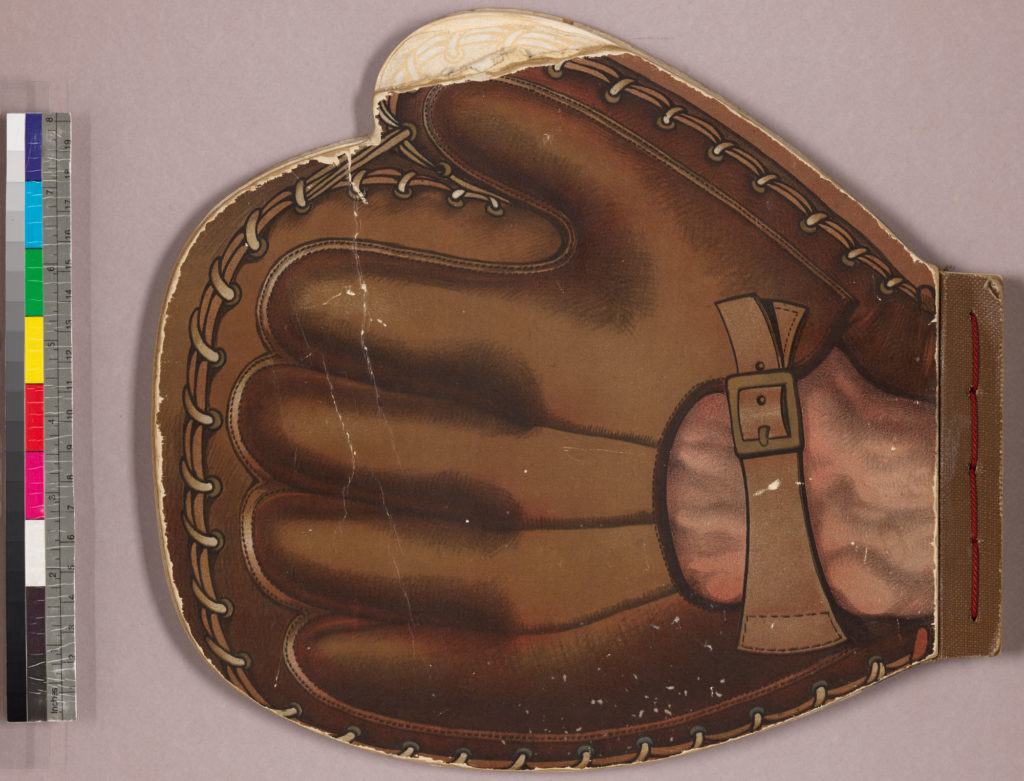
RBSC’s example of the Jackie Robinson doll apparently includes all of the original accessories that accompanied the doll. Housed in its original 15X15 inch square cardboard box, the doll wears a Brookyln Dodgers hat and jersey, uniform pants, socks, and shoes. The set also includes a wooden bat with a facsimile of Robinson’s signature, a promotional tag shaped like a glove, a plastic ball, a copy of the Jackie Robinson comic book, and a simple spinner-based Jackie Robinson baseball game.



The Jackie Robinson Doll is open and available to researchers during regular RBSC business hours. So stop by if you would like to “Play Ball with Jackie!”
Sources Cited
Tex McCrary and Jinx Falkenburg, “New York Up Close: Martin Stone, Lawyer in Show Business,” New York Herald Tribune 30 July, 1951, p. 7.
“Toy Fair Opened; 100,000 Items for the Yule Trade on View,” New York Herald Tribune 7 March 1950, p. 23.
“Jackie Robinson Doll and Life Story!” [advertisement], Alabama Tribune 15 December 1950, p. 6.
“Bill’s” [advertisement], Harrisburg Patriot News 2 July 1950, p. 44.
“Robinson Dolls at Macys,” [Lincoln, Nebraska] The Voice 6 May 1950, p. 3.
Previous Black History Month posts:
2025: Remembering the Harrisburg Trojans, Champion African American Football Team
2023: African American Women Activists and Athletes in 1970s Feminist Magazines
2021: Paul Laurence Dunbar’s New Literary Tradition Packaged to Sell