We join the Library of Congress, National Archives and Records Administration, National Endowment for the Humanities, National Gallery of Art, National Park Service, Smithsonian Institution, and United States Holocaust Memorial Museum in celebrating National Hispanic Heritage Month.
Migratory History from a Child’s Point of View
by Erika Hosselkus, Curator, Latin American Collections
In recognition of National Hispanic Heritage Month, we share this Migratory History of La Raza coloring book, printed in 1974 by El Renacimiento, a branch of the Lansing, Michigan publisher Renaissance Publications. Emerging from the city’s vibrant and active Chicano community, the coloring book narrates the history of the U.S. Chicano population in pictures and bilingual text, for Michigan’s Chicano youth. Michigan-based Chicano artist, David Torrez, produced both the history and the drawings included in the title, which is as much textbook and activist statement as coloring book.
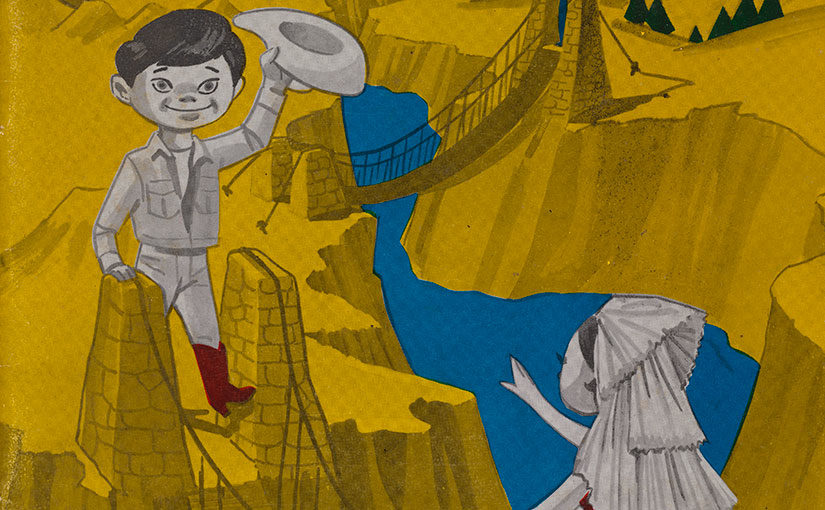
The coloring book’s activist stance and message are evident even from its cover. Printed on glossy cardstock, it features a Chicano boy, dressed in Southwestern clothing, smiling and waving to a young girl who stands on the other side of a river – most certainly the Rio Grande. The young girl is dressed in the traditional clothing and head covering of the Tehuana, a female cultural type associated with the Isthmus of Tehuantepec region of far southern Mexico. Through this image, Torrez links the U.S. Chicano population with residents of Mexico and extends Mexican cultural identity from the country’s border with Guatemala up into the United States – well beyond the country’s political boundaries. Two open and pleasant-looking bridges span the Rio Grand, connecting Mexican Americans and residents of Mexico and advocating friendship and camaraderie between them.

The Montcalm County Intermediate School District, located in Stanton, Michigan, an agricultural area located north of Lansing and home to significant populations of migrant workers in the 1970s, contributed to the development of the coloring book as part of a migrant education project. The border and two small birds on the title page might appear entirely decorative, but they are an appropriation of symbols of Mexican – even indigenous Mexican – identity. They are Aztec eagles and they frame publication details, including a statement that the book was “Printed in AZTLAN” – the birthplace of the Aztecs. Like many Chicano initiatives of this era, Michigan’s activists found resonance in these Native references that seemed devoid of European influence or content. Through the eagles and references to Aztlan, they harkened back to an idealized indigenous past.

Page 2 provides the children for whom this coloring book was created a brief, unbiased definition of “migrant child” in English and Spanish. It links the definition specifically to movement between school districts and to agricultural and food-processing industries, but not to race or ethnicity. The statement is a resource, or tool, to help migrant children consider and articulate identity as related to their mobile status.
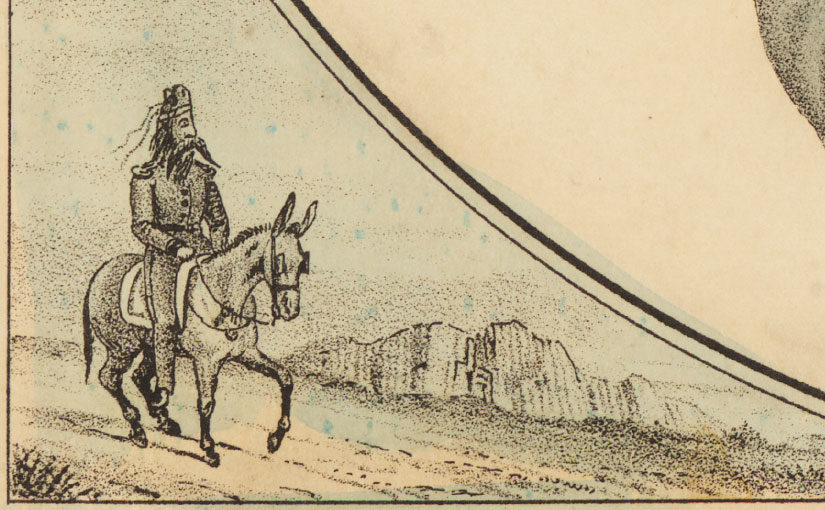
The inside of the coloring book recounts Chicano history by dedicating pages to each of the major indigenous groups of Mexico, depicting the events of the Spanish conquest of the Aztecs as well as highlights of modern Mexican history, and pointing to important issues of the day.


A page entitled “Contribution of the Migrant Workers” argues that, since 1900, migrant farm workers and their labor served as the basis of the U.S. economic structure. “Vida del Migratorio” observes that, despite this contribution, migrant housing is often substandard. This issue received attention from the federal government at the time that the coloring book was issued, though improvements for laborers were often slow and uneven.
Along with this source geared toward children, El Renacimiento produced a newspaper of the same name that focused on the Chicano Rights movement and was published in Lansing from the 1970s through 1990s. David Torrez and Edmundo Georgi, both contributors to this coloring book also work on the newspaper, El Renacimento, which can be consulted on microfilm here in the Hesburgh Libraries.
Related Previous Blog Posts:
- National Hispanic Heritage Month 2017: Sergio Sánchez Santamaría
- National Hispanic Heritage Month 2018: Puerto Rican Artists
- National Hispanic Heritage Month 2019: Latinx Ephemera Collection
- National Hispanic Heritage Month 2020: The Woodcuts of Consuelo Gotay